Mesh: Plasă pornind de la o Formă
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Meshes → Create Mesh from Shape |
| Workbenches |
| Mesh |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| None |
Description
Introducere
Această comandă creează o plasă dintr-un obiect tip formă.
The inverse operation is Part ShapeFromMesh from the Part Workbench.
Utilizare
- Selectați obiectul de tip formă.
- Alegeți Meshes →
Create Mesh from shape... din meniul principal.
- Un meniu va cere utilizarea mesher-ului/tessellation și valorile corespunzătoare pentru mesher
Doar selectând Meshes → Create Mesh from shape... vă va oferi un meniu suplimentar pentru a vă alege forma de transformat în plasă
Limitări
Abaterea de suprafață: Dacă acest număr este mai mic, ochiul devine mai fin. Valoarea cea mai mică este de 0,001.
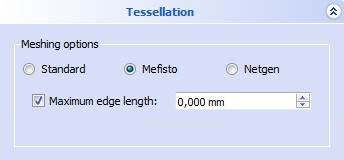
Puteți alege între plase fiind:
- Foarte grosieră
- Grosieră
- Moderat
- Fină
- Foarte fină
- Definită de utilizator
Pentru ca Mesh fiind "definit de utilizator", puteți seta aceste valori:
- Clasificarea dimensiunii ochiului: Dacă acest parametru este mai mic, ochiul devine mai fin. O valoare cuprinsă între 0,1 și 10.
- Element per muchie/edge: Dacă acest parametru este mai mare, ochiul devine mai fin. O valoare cuprinsă între 0,1 și 10.
- Element pe raza de curbură: Dacă acest parametru este mai mare, ochiul devine mai fin. O valoare cuprinsă între 0,1 și 10.
Pentru fiecare opțiune principală puteți de asemenea să alegeți:
- Optimizați suprafața: dacă va fi făcută optimizarea formei suprafeței.
- Elemente de ordine al doilea: Fie elementele de ordinul doi vor fi generate.
- Quad dominantă: Dacă ochiurile vor fi aranjate ca hexahedral.
Mefisto Mesher
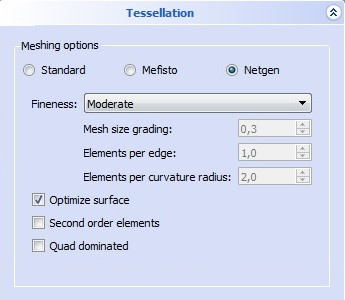
Netgen Mesher
- Fineness: select an options for the finesse of the mesh:
- Very coarse
- Coarse
- Moderate
- Fine
- Very fine
- User defined: for this option the following settings can be specified:
- Mesh size grading: a smaller value results in a finer mesh. The value must be in the
0.1-1.0range. - Element per edge: a larger value results in a finer mesh. The value must be in the
0.2-10.0range. - Element per curvature radius: a larger value results in a finer mesh. The value must be in the
0.2-10range.
- Mesh size grading: a smaller value results in a finer mesh. The value must be in the
- Optimize surface: if checked, the surface shape will be optimized.
- Second order elements: if checked, second order elements will be generated resulting in a finer mesh.
- Quad dominated: if checked, the mesh will preferably use quadrilateral faces.
Gmsh mesher
For Linux users: the external Gmsh module is required.
- Meshing: select a meshing option:
- Automatic
- Adaptive
- Delaunay
- Frontal
- BAMG
- Frontal Quad
- Parallelograms
- Max. element size: a smaller value results in a finer mesh. Specify
0to have this size automatically determined. - Min. element size: a smaller value results in a finer mesh. The value should be smaller than the Max. element size. Specify
0to have this size automatically determined. - Angle: seems to be unsupported at this time.
- Path: press the ... button and browse to the gmsh.exe path.
- If the meshing process takes too long you can press the Kill button to abort it.
- Press the Clear button to remove the information in the text area.
Notes
- This command is not restricted to objects created with the Part workbench. It can create a mesh from any object that has a shape including objects created with the PartDesign workbench.
- The Std Export command can export shape objects directly to a mesh format.
- See also: Export to STL or OBJ tutorial.
Preferences
Standard mesher
- The Surface deviation setting is stored: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Mesh → Meshing → Standard → LinearDeflection.
- The Angular deviation setting is stored: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Mesh → Meshing → Standard → AngularDeflection.
- The Relative surface deviation setting is stored: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Mesh → Meshing → Standard → RelativeLinearDeflection.
Gmsh mesher
- The Path is stored: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Mesh → Meshing → gmshExe.
Properties
See: Mesh Feature.
Scripting
See also: FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
To create a mesh object from a shape object use the meshFromShape method of the MeshPart module. This method has several signatures. The signature determines the mesher that will be used. The example below uses the Mefisto mesher signature.
import FreeCAD, Part, Mesh, MeshPart
cyl = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Cylinder","Cylinder")
FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.recompute()
msh = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.addObject("Mesh::Feature", "Mesh")
msh.Mesh = MeshPart.meshFromShape(Shape=cyl.Shape, MaxLength=1)
msh.ViewObject.DisplayMode = "Flat Lines"
- Miscellaneous: Import mesh, Export mesh, Create mesh from shape, Regular solid, Unwrap Mesh, Unwrap Face
- Modifying: Harmonize normals, Flip normals, Fill holes, Close hole, Add triangle, Remove components, Remove components by hand, Smooth, Refinement, Decimation, Scale
- Boolean: Union, Intersection, Difference
- Cutting: Cut mesh, Trim mesh, Trim mesh with a plane, Create section from mesh and plane, Cross-sections
- Components and segments: Merge, Split by components, Create mesh segments, Create mesh segments from best-fit surfaces
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub