Sketcher Workbench

Introducere
Atelierul Sketcher Workbench este utilizat pentru a crea forme geometrice 2D cu intenția de a le utiliza în Atelierul PartDesign Workbench, Arch Workbench, și alte ateliere. În general, o geometrie 2D este considerată punctul de plecare pentru majoritatea modelelor CAD, deoarece o schiță 2D poate fi "extrudată" pentru a crea o formă 3D; mai mult, schițele 2D pot fi folosite pentru a crea alte caracteristici cum ar fi cavități, creste sau extrudări peste formele 3D construite anterior. Împreună cu operațiile booleene pe solide definite în Part Workbench, Sketcher-ul formează nucleul de design generativ al formei solide.
Together with boolean operations defined in the Part Workbench, the Sketcher Workbench, or "The Sketcher" for short, forms the basis of the constructive solid geometry (CSG) method of building solids. Together with
PartDesign Workbench operations, it also forms the basis of the feature editing methodology of creating solids. But many other workbenches use sketches as well.
Atelierul de lucru Sketcher pune pe primul loc ”constrângerile” - permițând definirea formelor 2D după criterii geometrice precise. Un solver matematic de constrângeri calculează nivelul constrângerii și permite explorarea interactivă a gradelor de libertate.
La ce nu este bun Sketcher-ul
Instrumentul Sketcher nu este destinat pentru realizarea planurilor 2D. Odată ce schițele sunt folosite pentru a genera o caracteristică solidă, ele sunt ascunse automat. Constrângerile sunt vizibile numai în modul Editare schiță.
A fully constrained sketch
Constraints
Ce sunt constrângerile?
În loc de dimensiuni, constrângerile sunt folosite pentru a limita gradul de libertate al unui obiect. De exemplu, o linie fără constrângeri are 4 Degrees of Freedom (abreviat ca "DOF"): poate fi mișcat orizontal sau vertical, poate fi întinsă și poate fi rotită.
Aplicarea unei constrângeri orizontale sau verticale sau a unei constrângeri de unghi (relativ la o altă linie sau la una dintre axe) va limita capacitatea sa de a se roti, lăsându-l astfel cu 3 grade de libertate. Blocarea unuia dintre punctele sale în raport cu originea va elimina încă 2 grade de libertate. Și aplicarea unei constrângeri de dimensiune va elimina ultimul grad de libertate. Linia este apoi considerată complet constrânsă .
Obiectele multiple pot fi constrânse între ele. Două linii pot fi unite prin unul dintre punctele lor cu constrângerea punctului coincident. Un unghi poate fi setat între ele sau poate fi setat perpendicular. O linie poate fi tangentă la un arc sau un cerc și așa mai departe. O schiță complexă, cu obiecte multiple, va avea o serie de soluții diferite, ceea ce înseamnă că "una dintre aceste soluții posibile a fost atinsă pe baza constrângerilor aplicate.
Există două tipuri de constrângeri: geometrice și dimensionale. Acestea sunt detaliate în secțiunea 'Instrumentele' de mai jos.
Edit constraints
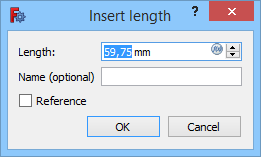
When a driving dimensional constraint is created, and if the Ask for value after creating a dimensional constraint preference is selected (default), a dialog opens to edit its value.
You can enter a numerical value or an expression, and it is possible to name the constraint to facilitate its use in other expressions. You can also check the Reference checkbox to switch the constrain to reference mode.
To edit the value of an existing dimensional constraint do one of the following:
- Double-click the constraint value in the 3D view.
- Double-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog.
- Right-click the constraint in the Sketcher Dialog and select the Change value option from the context menu.
Reposition constraints
Dimensional constraints can be repositioned in the 3D view by dragging. Hold down the left mouse button over the constraint value and move the mouse. The symbols of geometric constraints are positioned automatically and cannot be moved.
Profile sketches
To create a sketch that can be used as a profile for generating solids certain rules must be followed:
- The sketch must contain only closed contours. Gaps between endpoints, however small, are not allowed.
- Contours can be nested, to create voids, but should not self-intersect or intersect other contours.
- Contours cannot share edges with other contours. Duplicate edges must be avoided.
- T-connections, that is more than two edges sharing a common point, or a point touching an edge, are not allowed.
These rules do not apply to construction geometry (default color blue), which is not shown outside edit mode, or if the sketch is used for a different purpose. Depending on the workbench and the tool that will use the profile sketch, additional restrictions may apply.
Drawing aids
The Sketcher Workbench has several drawing aids and other features that can help when creating geometry and applying constraints.
Continue modes
There are two continue modes: Geometry creation "Continue Mode" and Constraint creation "Continue Mode". If these are checked (default) in the preferences, related tools will restart after finishing. To exit a continuous tool press Esc or the right mouse button. This must be repeated if a continuous geometry tool has already received input. You can also exit a continuous tool by starting another geometry or constraint creation tool. Note that pressing Esc if no tool is active will exit sketch edit mode. Uncheck the Esc can leave sketch edit mode preference if you often inadvertently press Esc too many times.
Auto constraints
In sketches that have Auto constraints checked (default) several constraints are applied automatically. The icon of a proposed automatic constraint is shown next to the cursor when it is placed correctly. Left-Clicking will then apply that constraint. This is a per-sketch setting that can be changed in the Sketcher Dialog or by changing the VizualizareAutoconstraints property of the sketch.
The following constraints are applied automatically:
Coincident
Point on object
Horizontal
Vertical
Tangent
- introduced in version 1.0:
Symmetric (line midpoint)
Snapping
It is possible to snap to grid lines and grid intersection, to edges of geometry and midpoints of lines and arcs, and to certain angles. Please note that snapping does not produce constraints in and of itself. For example, only if Auto constraints is switched on will snapping to an edge produce a Point on object constraint. But just picking a point on the edge would then have the same result.
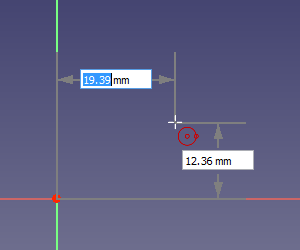
On-View-Parameters
Depending on the selected option in the preferences only the dimensional On-View-Parameters or both the dimensional and the positional On-View-Parameters can be enabled. Positional parameters allow the input of exact coordinates, for example the center of a circle, or the start point of a line. Dimensional parameters allow the input of exact dimensions, for example the radius of a circle, or the length and angle of a line. On-View-Parameters are not available for all tools.
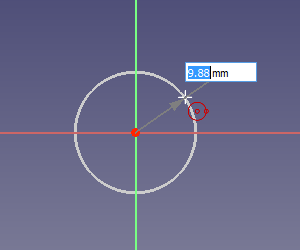
Determining the center point of a circle with the positional parameters enabled
Determining the radius of a circle with the dimensional parameters enabled
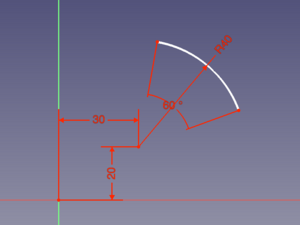
If values are entered and confirmed by pressing Enter or Tab, related constraints are added automatically. If two parameters are displayed at the same time, for example the X and Y coordinate of a point, it is possible to enter one value and pick a point to define the other. Depending on the object additional constraints may be required to fully constrain it. Constraints resulting from On-View-Parameters take precedence over those that may result from Auto constraints.
Arc created by entering all On-View-Parameters with resulting automatically created constraints
Coordinate display
If the Show coordinates beside cursor while editing preference is checked (default), the parameters of the current geometry tool (coordinates, radius, or length and angle) are displayed next to the cursor. This is deactivated while On-View-Parameters are shown.
Selection methods
While a sketch is in edit mode the following selection methods can be used:
3D view element selection
As elsewhere in FreeCAD, an element can be selected in the 3D view with a single left mouse click. But there is no need to hold down the Ctrl key when selecting multiple elements. Holding down that key is possible though and has the advantage that you can miss-click without losing the selection. Edges, points and constraints can be selected in this manner.
3D view box selection
Box selection in the 3D view works without using Std BoxSelection or Std BoxElementSelection:
- Make sure that no tool is active.
- Do one of the following:
- Click in an empty area and drag a rectangle from left to right to select elements that lie completely inside the rectangle.
- Click in an empty area and drag a rectangle from right to left to also select elements that touch or cross the rectangle.
You can box-select edges and points, constraints cannot be box-selected.
3D view connected geometry selection
Double-clicking an edge in the 3D view will select all edges directly and indirectly connected with that edge via endpoints. There is no need for the edges to be connected with Coincident constraints, endpoints need only have the same coordinates.
Sketcher Dialog selection
Edges and points can also be selected from the Elements section of the Sketcher Dialog, and constraints from the Constraints section of that dialog.
Copy, cut and paste
The standard keyboard shortcuts, Ctrl+C, Ctrl+X and Ctrl+V, can be used to copy, cut and paste selected Sketcher geometry including related constraints. But these tools are also available from the Sketch → Sketcher tools menu. They can be used within the same sketch but also between different sketches or separate instances of FreeCAD. Since the data is copied to the clipboard in the form of Python code, it can be used in other ways too (e.g. shared on the forum).
Tools
Instrumentele
Instrumentele Sketcher Workbench sunt toate localizate în meniul Sketch care apare atunci când încărcați Sketcher Workbench.
Some tools are also available from the 3D view context menu while a sketch is in edit mode, or from the context menus of the Sketcher Dialog.
introduced in version 0.21: If a sketch is in edit mode the Structure toolbar is hidden as none of its tools can then be used.
General
Sketcher toolbar
 New sketch:Creează o nouă schiță pe o fațetă sau pe un plan selectat. Dacă nu este selectată nici o fațetă în timp ce acest instrument este executat, utilizatorul este chemat să selecteze un plan dintr-o fereastră pop-up.
New sketch:Creează o nouă schiță pe o fațetă sau pe un plan selectat. Dacă nu este selectată nici o fațetă în timp ce acest instrument este executat, utilizatorul este chemat să selecteze un plan dintr-o fereastră pop-up.
 Edit sketch: Editează schița selectată.
Edit sketch: Editează schița selectată.
 Map sketch to face: Aplică o schiță pe o fațetă a unui solid.
Map sketch to face: Aplică o schiță pe o fațetă a unui solid.
- Reorient sketch: Permite schimbarea poziției schiței
- Validate sketch: Verifică toleranța la direferite puncte și le ajustează.
 Merge sketches: Fuzionează două sau mai multe schițe. introduced in version 0.15
Merge sketches: Fuzionează două sau mai multe schițe. introduced in version 0.15
 Mirror sketch: Crează o schiță simetrică după axa x, y sau față de origine. introduced in version 0.16
Mirror sketch: Crează o schiță simetrică după axa x, y sau față de origine. introduced in version 0.16
Sketcher Edit Mode toolbar
 Leave sketch: Părăsește modul de editare al Sketch.
Leave sketch: Părăsește modul de editare al Sketch.
 View sketch: Setează modul de vedere perpendicular pe planul schiței.
View sketch: Setează modul de vedere perpendicular pe planul schiței.
 View section: Creează o secțiune plană care ascunde temporar orice lucru în fața planului schiței. introduced in version 0.18
View section: Creează o secțiune plană care ascunde temporar orice lucru în fața planului schiței. introduced in version 0.18
Sketcher edit tools toolbar
Toggle grid: Toggles the grid in the sketch currently being edited. Settings can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Toggle snap: Toggles snapping in all sketches. Settings can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Configure rendering order: The rendering order of all sketches can be changed in the related menu. introduced in version 0.21
Other
Stop operation: Stops any currently running geometry or constraint creation tool.
Sketcher geometries
Aceste unelte se folosesc la crearea obiectelor.
 Point: Desenează un punct.
Point: Desenează un punct.
 Polyline (multiple-point line): Creează o linie formată din mai multe segmente de linie. Apăsând tasta M în timp ce desenați o polilinie comută între diferite moduri de polilinie.
Polyline (multiple-point line): Creează o linie formată din mai multe segmente de linie. Apăsând tasta M în timp ce desenați o polilinie comută între diferite moduri de polilinie.
 Line by 2 point: Desenează un segment de linie definit prin 2 puncte. Liniile sunt infinite în ceea ce privește anumite constrângeri.
Line by 2 point: Desenează un segment de linie definit prin 2 puncte. Liniile sunt infinite în ceea ce privește anumite constrângeri.
 Arc: Desenează un segemnt de cerc definit prin centru, radius, unghiul de stat și cel de capăt.
Arc: Desenează un segemnt de cerc definit prin centru, radius, unghiul de stat și cel de capăt.
 Arc by 3 Point: Desenează un segment de arc de cerc din două puncte de capăt și un alt punct de pe circumferință.
Arc by 3 Point: Desenează un segment de arc de cerc din două puncte de capăt și un alt punct de pe circumferință.
Arc of ellipse: Creates an arc of ellipse.
Arc of hyperbola: Creates an arc of hyperbola.
Arc of parabola: Creates an arc of parabola.
 Circle: Desenează un cerc definit prin centru și rază.
Circle: Desenează un cerc definit prin centru și rază.
 Circle by 3 Point: Desenează un cerc definit prin trei puncte pe circumferință.
Circle by 3 Point: Desenează un cerc definit prin trei puncte pe circumferință.
Ellipse by center: Creates an ellipse by its center, an endpoint of one of its axes, and a point along the ellipse. introduced in version 1.0: Or by both endpoints of one of its axes and a point along the ellipse.
Ellipse by 3 points: Creates an ellipse by the endpoints of one of its axes and a point along the ellipse. introduced in version 1.0: This is the same tool as Ellipse by center but with a different initial mode.
 Rectangle: Desenează un dreptunghi definit prin 2 puncte diagonal opuse.
Rectangle: Desenează un dreptunghi definit prin 2 puncte diagonal opuse.
Centered rectangle: Creates a centered rectangle. introduced in version 1.0: This is the same tool as Rectangle but with a different initial mode.
Rounded rectangle: Creates a rounded rectangle. Idem.
 Triangle: Desenează un triunghi echilateral inscris într-un cerc .introduced in version 0.15
Triangle: Desenează un triunghi echilateral inscris într-un cerc .introduced in version 0.15
 Square: Desenează un pătrat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
Square: Desenează un pătrat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
 Pentagon: Desenează un pentagon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
Pentagon: Desenează un pentagon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
 Hexagon: Desenează un hexagon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
Hexagon: Desenează un hexagon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
 Heptagon: Desenează un heptagon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
Heptagon: Desenează un heptagon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
 Octagon: Desenează un octogon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
Octagon: Desenează un octogon regulat înscris într-un cerc. introduced in version 0.15
 Create Regular Polygon : Desenează un poligon regulat prin selectarea numărului de laturi și a două puncte: centrul, respectiv unul dintre unghiuri.
Create Regular Polygon : Desenează un poligon regulat prin selectarea numărului de laturi și a două puncte: centrul, respectiv unul dintre unghiuri.
 Slot: Desenează un oval (locaș de pană) prin selectare centrului unui semicerc, a razei și un punct de capăt al celuilalt semicerc.
Slot: Desenează un oval (locaș de pană) prin selectare centrului unui semicerc, a razei și un punct de capăt al celuilalt semicerc.
Arc slot: Creates an arc slot. introduced in version 1.0
B-spline by control points: Creates a B-spline curve by control points. introduced in version 1.0: Or by knot points.
Periodic B-spline by control points: Creates a periodic (closed) B-spline curve by control points. introduced in version 1.0: This is the same tool as B-spline by control points but with a different initial mode.
B-spline by knots: Creates a B-spline curve by knot points. Idem.
Periodic B-spline by knots: Creates a periodic (closed) B-spline curve by knot points. Idem.
 Construction Mode: Comută elementele geometrice ale schiței de la / la modul de Construcție. Forma geometrică este afișată în albastru și nu este luată în considerare în afara modului de editare a schiței.
Construction Mode: Comută elementele geometrice ale schiței de la / la modul de Construcție. Forma geometrică este afișată în albastru și nu este luată în considerare în afara modului de editare a schiței.
Constrângeri Sketcher
Constrângerile sunt folosite pentru a defini lungimile, a stabili reguli între elementele de schiță și pentru a bloca schița de-a lungul axelor verticale și orizontale. Unele constrângeri necesită utilizarea Helper constraints.
Dimension: Is the context-sensitive constraint tool of the Sketcher Workbench. Based on the current selection, it offers appropriate dimensional constraints, but also geometric constraints. introduced in version 1.0
Fixează distanța orizontală dintre două puncte sau puncte finale. Dacă este selectat un singur element, distanța este setată față de origine.
Fixează distanța verticală între 2 puncte sau puncte de capăt ale liniei. Dacă este selectat un singur element, distanța este setată față de origine.
Definește distanța unei linii selectate prin limitarea lungimii acesteia sau definește distanța dintre două puncte prin limitarea distanței dintre ele.
Auto radius/diameter: Fixes the radius of arcs and B-spline weight circles, and the diameter of circles.
Definește raza unui arc de cerc sau cerc selectat prin limitarea razei.
Definește unghiul interior dintre două linii selectate.
Diameter: Fixes the diameter of circles and arcs.
Angle: Fixes the angle between two edges, the angle of a line with the horizontal axis of the sketch, or the aperture angle of a circular arc.
 Lock: Restricționează elementul selectat prin stabilirea distanțelor orizontale și orizontale față de origine, blocând astfel locația acelui element. Aceste distanțe de constrângere pot fi editate mai târziu.
Lock: Restricționează elementul selectat prin stabilirea distanțelor orizontale și orizontale față de origine, blocând astfel locația acelui element. Aceste distanțe de constrângere pot fi editate mai târziu.
Coincident (unified): Creates a coincident constraint between points, fixes points on edges or axes, or creates a concentric constraint. It combines the Coincident and Point on object tools. introduced in version 1.0
 Coincident: Creează o constrângere de coincidență cu unul sau mai multe puncte.
Coincident: Creează o constrângere de coincidență cu unul sau mai multe puncte.
 Point On Object: Face să coincidă un punct cu altul cu alt obiect ca de ex: linie, arc, sau axă.
Point On Object: Face să coincidă un punct cu altul cu alt obiect ca de ex: linie, arc, sau axă.
Horizontal/vertical: Constrains lines or pairs of points to be horizontal or vertical, whichever is closest to the current alignment. It combines the Horizontal and Vertical tools. introduced in version 1.0
Constrânge liniile selectate sau elementele de polilinie la o orientare orizontală reală. Pot fi selectate mai multe obiecte înainte de aplicarea acestei constrângeri.
 Vertical: Constrâne liniile selectate sau elementele poliliniei la o orientare verticală. Se poate aplică la mai mult de un obiect.
Vertical: Constrâne liniile selectate sau elementele poliliniei la o orientare verticală. Se poate aplică la mai mult de un obiect.
 Parallel: Constrânge două sau mai multe linii a fi paralele înte ele.
Parallel: Constrânge două sau mai multe linii a fi paralele înte ele.
 Perpendicular: Constrânge două linii a fi perpendiculare una pe ceallată, sau consrînge o linie a fi perpendiculară pe un capăt de arc de cerc.
Perpendicular: Constrânge două linii a fi perpendiculare una pe ceallată, sau consrînge o linie a fi perpendiculară pe un capăt de arc de cerc.
 Tangent: Creează o constrângere de tangență în două entități selectate ates, sau o constrânere de coliniaritaea între două segmente de linie. Un segment de linie nu trebuie să stea direct pe un arc sau un cerc pentru a fi constrâns tangent la acel arc sau cerc.
Tangent: Creează o constrângere de tangență în două entități selectate ates, sau o constrânere de coliniaritaea între două segmente de linie. Un segment de linie nu trebuie să stea direct pe un arc sau un cerc pentru a fi constrâns tangent la acel arc sau cerc.
 Equal Length: Constrânge două entități selectate a fi egale una cu celălaltă. Dacă sunt utilizate pe cercuri sau arce de cerc, raza lor va fi egală.
Equal Length: Constrânge două entități selectate a fi egale una cu celălaltă. Dacă sunt utilizate pe cercuri sau arce de cerc, raza lor va fi egală.
 Symmetric:Constrânge două puncte a fi simetrice față de o linie sau constrânge primele două puncte selectate a fi simetrice în raport cu un al treilea punct selectat.
Symmetric:Constrânge două puncte a fi simetrice față de o linie sau constrânge primele două puncte selectate a fi simetrice în raport cu un al treilea punct selectat.
Practic permite blocarea unui element geometric în loc cu o singură constrângere. Ar trebui să fie deosebit de util să lucrați cu acest la curbele B-Splines. A se vedea Block Constraint forum topic. introduced in version 0.17
 Snell's Law: Constrânge două linii pentru a se supune unei legi de refracție pentru a simula lumina care traversează o interfață. introduced in version 0.15
Snell's Law: Constrânge două linii pentru a se supune unei legi de refracție pentru a simula lumina care traversează o interfață. introduced in version 0.15
 Toggle reference/driving constraint: Comută bara de instrumente sau constrângerile selectate de la/din modul de referință. introduced in version 0.16
Toggle reference/driving constraint: Comută bara de instrumente sau constrângerile selectate de la/din modul de referință. introduced in version 0.16
Activate/deactivate constraint: Activates or deactivates selected constraints.
Instrumente Sketcher
 Fillet: Face o racordare între două linii îmbinate într-un punct. Selectați ambele linii sau faceți clic pe punctul de intersecție, apoi activați instrumentul.
Fillet: Face o racordare între două linii îmbinate într-un punct. Selectați ambele linii sau faceți clic pe punctul de intersecție, apoi activați instrumentul.
Chamfer: creates a chamfer between two non-parallel edges. This is the same tool as Fillet but with a different initial mode. introduced in version 1.0
 Trimming: Ajustează o linie, un cerc sau un arc în raport cu amplasarea unui punct dat(poziția mouse-ului).
Trimming: Ajustează o linie, un cerc sau un arc în raport cu amplasarea unui punct dat(poziția mouse-ului).
Split: Splits an edge while transferring most constraints.
Extend: Extinde o linie sau un arc de cerc până la o limită definită printr-un arc de cerc, elipsă, arc de elipsă sau un punct în spațiu. introduced in version 0.17
 External Geometry: Creează o margine legată de geometria exterioară.
External Geometry: Creează o margine legată de geometria exterioară.
CarbonCopy: Copiază forma geometrică din altă schiță.introduced in version 0.17
 Select Origin: Selectează originea unei sketch introduced in version 0.15
Select Origin: Selectează originea unei sketch introduced in version 0.15
 Select Horizontal Axis: Selectează axa orizontală a sketch introduced in version 0.15
Select Horizontal Axis: Selectează axa orizontală a sketch introduced in version 0.15
 Select Vertical Axis: Selectează axa verticală a sketch introduced in version 0.15
Select Vertical Axis: Selectează axa verticală a sketch introduced in version 0.15
Array transform: Moves or optionally creates copies of selected elements. introduced in version 1.0
Polar transform: Rotates or optionally creates rotated copies of selected elements. introduced in version 1.0
Scale transform: Scales or optionally creates scaled copies of selected elements. introduced in version 1.0
Offset geometry: Creates equidistant edges around selected edges. introduced in version 1.0
 Symmetry: Copiază elementul simetric față de o linie selectatăe introduced in version 0.16
Symmetry: Copiază elementul simetric față de o linie selectatăe introduced in version 0.16
Remove axes alignment: Removes the axes alignment of selected edges by replacing Horizontal and Vertical constraints with Parallel and Perpendicular constraints.
Delete All Geometry: Șterger toate elementele geometrice din sketch. introduced in version 0.18
Delete All Constraints: Șterge toate constrângerile din sketch. introduced in version 0.18
Copy in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Cut in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Paste in Sketcher: See Copy, cut and paste.
Instrumentele pentru Sketcher B-spline
Decrease B-spline degree: Decreases the degree (order) of B-splines.
Insert knot: Inserts a knot into a B-spline or increases the multiplicity of an existing knot.
Join curves: Creates a B-spline by joining two existing B-splines or other edges. introduced in version 0.21
Sketcher visual
Select solver DOFs: Evidențiază în verde geometria cu grade de libertate (DOF), adică nu este complet constrânsă. introduced in version 0.18
 Select Constraints: Selectează constrângerile elementului Sketcher introduced in version 0.15
Select Constraints: Selectează constrângerile elementului Sketcher introduced in version 0.15
 Select Elements Associated with constraints: Selectați elementele sketcher asociate cu constrângerile introduced in version 0.15
Select Elements Associated with constraints: Selectați elementele sketcher asociate cu constrângerile introduced in version 0.15
 Select Redundant Constraints: Selectează constrângeri redundante a sketch introduced in version 0.15
Select Redundant Constraints: Selectează constrângeri redundante a sketch introduced in version 0.15
 Select Conflicting Constraints: Selectează constrângerile conflictuale ale unei sketch introduced in version 0.15
Select Conflicting Constraints: Selectează constrângerile conflictuale ale unei sketch introduced in version 0.15
Show/hide circular helper for arcs: Shows or hides the circular helpers (underlying virtual circles) for arcs in all sketches. introduced in version 1.0
Show/hide B-spline control point weight: Shows or hides the B-spline control point weight in all sketches.
 Show/Hide internal geometry: Reface pierderea / ștergerea geometriei interne inutile a unei elipse selectate, arcului de elipsă / hyperbola / parabola sau B-spline.
Show/Hide internal geometry: Reface pierderea / ștergerea geometriei interne inutile a unei elipse selectate, arcului de elipsă / hyperbola / parabola sau B-spline.
 Switch Virtual Space: Vă permite să comutați între a ”ascunde” constrângerile și a le face iarăși vizibile. introduced in version 0.17 See https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26614
Switch Virtual Space: Vă permite să comutați între a ”ascunde” constrângerile și a le face iarăși vizibile. introduced in version 0.17 See https://forum.freecadweb.org/viewtopic.php?f=9&t=26614
Obsolete tools
 Clone: Clonează un element sketcher introduced in version 0.16
Clone: Clonează un element sketcher introduced in version 0.16
 Close Shape: Creează o formă închisă prin aplicarea unor constrângeri de coincidență a punctelor de capătintroduced in version 0.15
Close Shape: Creează o formă închisă prin aplicarea unor constrângeri de coincidență a punctelor de capătintroduced in version 0.15
Corner-preserving fillet: Creates a fillet between two non-parallel lines while preserving their corner point. Not available in version 1.0 and above.
 Connect Edges: Conectați elementele Sketcher aplicând constrângeri de coincidentență la punctele de capăt introduced in version 0.15
Connect Edges: Conectați elementele Sketcher aplicând constrângeri de coincidentență la punctele de capăt introduced in version 0.15
 Copy: Copiază un element sketcher introduced in version 0.16
Copy: Copiază un element sketcher introduced in version 0.16
Move: Mută elementul geometric ales luând ca referință ultimul punct selectat.introduced in version 0.18
 Rectangular Array: Creează o matrice de multiplicare a elementelor sketcher selectate introduced in version 0.16
Rectangular Array: Creează o matrice de multiplicare a elementelor sketcher selectate introduced in version 0.16
Preferințe
 Preferences...: Preferințe disponibile în Sketcher Tools.
Preferences...: Preferințe disponibile în Sketcher Tools.
Best practices
Cele mai bune practici
Fiecare utilizator CAD își dezvoltă în timp propriul mod de a lucra, dar există câteva principii generale utile care trebuie urmate.
- O serie de schițe simple sunt mai ușor de gestionat decât una complexă. De exemplu, o primă schiță poate fi creată pentru funcționalitate 3D de bază (fie un pad, fie o rotire), în timp ce a doua poate conține găuri sau decupări (buzunare). Unele detalii pot fi lăsate, pentru a fi realizate ulterior ca elemente 3D. Puteți alege să evitați filamentele din schiță dacă există prea multe și adăugați-le ca o funcționalitate 3D.
- Creați întotdeauna un profil închis, sau schița dvs. nu va produce un solid, ci mai degrabă un set de fețe deschise. Dacă nu doriți ca unele obiecte să fie incluse în creația solidă, transformați-le în elementele de construcție cu instrumentul Mod de construcție.
- Utilizați caracteristica de constrângeri automate pentru a limita numărul de constrângeri pe care trebuie să le adăugați manual.
- Ca regulă generală, aplicați mai întâi constrângeri geometrice, apoi constrângeri dimensionale și blocați ultima schiță. Dar amintiți-vă: regulile sunt făcute pentru a fi încălcate. Dacă întâmpinați dificultăți în manipularea schiței dvs., poate fi util să restrângeți mai întâi câteva obiecte înainte de a vă completa profilul.
- Dacă este posibil, centrați schița la origine (0,0) cu constrângerea de blocare. Dacă schița dvs. nu este simetrică, localizați unul dintre punctele sale la origine sau alegeți numere rotunde frumoase pentru distanțele de blocare. În v0.12, constrângerile externe (constrângerea schiței față de geometria 3D existentă ca marginile sau alte schite) nu sunt implementate. Aceasta înseamnă că pentru a localiza geometria schițelor care urmează în prima schiță, va trebui să setați manual distanțele față de prima schiță. O constrângere de blocare a (25,75) de origine este mai ușor de reținut decât (23,47,73.02).
- Dacă aveți posibilitatea de a alege între constrângerile de lungime și constrângerile orizontale sau verticale, preferați ultima. Constrângerile orizontale și verticale sunt mai puțin costisitoare ca timp computațional.
- În general, cele mai bune constrângeri de utilizat sunt: Constrângerile orizontale și verticale; Restricții de lungime orizontală și verticală; Point-to-Point Tangency. Dacă este posibil, limitați utilizarea acestora: restricția generală a lungimii; Tangența de la muchie la muchie; Fix Point pe o linie Constrângere; Constrângerea simetrice.
Tutoriale
- Sketcher Lecture by chrisb. This is a more than 80 page PDF document that serves as a detailed manual for the Sketcher. It explains the basics of Sketcher usage, and goes into a lot of detail about the creation of geometrical shapes, and each of the constraints.
- Basic Sketcher Tutorial for beginners
- Sketcher Micro Tutorial - Constraint Practices
- Sketcher requirement for a sketch Minimum requirement for a sketch and Complete determination of a sketch
Scripting
The Sketcher scripting page contains examples on how to create constraints from Python scripts.
Examples
For some ideas of what can be achieved with Sketcher tools, have a look at: Sketcher examples.


- General: Create sketch, Edit sketch, Attach sketch, Reorient sketch, Validate sketch, Merge sketches, Mirror sketch, Leave sketch, View sketch, View section, Toggle grid, Toggle snap, Configure rendering order, Stop operation
- Sketcher geometries: Point, Polyline, Line, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Arc of ellipse, Arc of hyperbola, Arc of parabola, Circle, Circle by 3 points, Ellipse, Ellipse by 3 points, Rectangle, Centered rectangle, Rounded rectangle, Triangle, Square, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Regular polygon, Slot, Arc slot, B-spline by control points, Periodic B-spline by control points, B-spline by knots, Periodic B-spline by knots, Toggle construction geometry
- Sketcher constraints:
- Dimensional constraints: Dimension, Horizontal distance, Vertical distance, Distance, Auto radius/diameter, Radius, Diameter, Angle, Lock
- Geometric constraints: Coincident (unified), Coincident, Point on object, Horizontal/vertical, Horizontal, Vertical, Parallel, Perpendicular, Tangent or collinear, Equal, Symmetric, Block
- Other constraints: Refraction (Snell's law)
- Constraint tools: Toggle driving/reference constraint, Activate/deactivate constraint
- Sketcher tools: Fillet, Chamfer, Trim, Split, Extend, External geometry, Carbon copy, Select origin, Select horizontal axis, Select vertical axis, Array transform, Polar transform, Scale transform, Offset geometry, Symmetry, Remove axes alignment, Delete all geometry, Delete all constraints
- Sketcher B-spline tools: Convert geometry to B-spline, Increase B-spline degree, Decrease B-spline degree, Increase knot multiplicity, Decrease knot multiplicity, Insert knot, Join curves
- Sketcher visual: Select unconstrained DoF, Select associated constraints, Select associated geometry, Select redundant constraints, Select conflicting constraints, Show/hide circular helper for arcs, Show/hide B-spline degree, Show/hide B-spline control polygon, Show/hide B-spline curvature comb, Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity, Show/hide B-spline control point weight, Show/hide internal geometry, Switch virtual space
- Additional: Sketcher Dialog, Preferences, Sketcher scripting
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub