Part Box
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Part → Primitives → Cube |
| Workbenches |
| Part |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| Part Primitives |
Description
The Part Box command creates a parametric box solid, a rectangular cuboid. In the coordinate system defined by its DataPlacement property, the bottom face of the box lies on the XY plane with its front left corner at the origin, and its front edge parallel to the X axis.
Usage
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Press the
Cube button.
- Select the Part → Primitives →
Cube option from the menu.
- Press the
- The box is created.
- Optionally change the dimensions and DataPlacement of the box by doing one of the following:
- Double-click the object in the Tree view:
- The Geometric Primitives task panel opens.
- Change one or more properties.
- The object is dynamically updated in the 3D view.
- Press the OK button.
- Change the properties in the Property editor.
- Change the DataPlacement with the
Std TransformManip command.
- Double-click the object in the Tree view:
Example
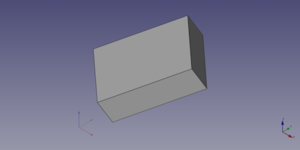
A Part Box object created with the scripting example below is shown here.
Notes
- A Part Box can also be created with the
Part Primitives command. With that command you can specify the dimensions and placement at creation time.
Properties
See also: Property editor.
A Part Box object is derived from a Part Feature object and inherits all its properties. It also has the following additional properties:
Data
Attachment
The object has the same attachment properties as a Part Part2DObject.
Box
- DataLength (
Length): The length of the box. This is the dimension in its X direction. The default is10mm. - DataWidth (
Length): The width of the box. This is the dimension in its Y direction. The default is10mm. - DataHeight (
Length): The height of the box. This is dimension in its Z direction. The default is10mm.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation, Part scripting and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
A Part Box can be created with the addObject() method of the document:
box = FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.addObject("Part::Box", "myBox")
- Where
"myBox"is the name for the object. - The function returns the newly created object.
Example:
import FreeCAD as App
doc = App.activeDocument()
box = doc.addObject("Part::Box", "myBox")
box.Length = 4
box.Width = 8
box.Height = 12
box.Placement = App.Placement(App.Vector(1, 2, 3), App.Rotation(75, 60, 30))
doc.recompute()
- Primitives: Box, Cylinder, Sphere, Cone, Torus, Tube, Create primitives, Shape builder
- Creation and modification: Create sketch, Extrude, Revolve, Mirror, Scale, Fillet, Chamfer, Make face from wires, Ruled Surface, Loft, Sweep, Section, Cross sections, 3D Offset, 2D Offset, Thickness, Projection on surface, Color per face
- Boolean: Make compound, Explode compound, Compound Filter, Boolean, Cut, Union, Intersection, Connect objects, Embed object, Cutout for object, Boolean fragments, Slice apart, Slice to compound, Boolean XOR, Check geometry, Defeaturing
- Other tools: Import CAD file, Export CAD file, Box selection, Create shape from mesh, Create points object from geometry, Convert to solid, Reverse shapes, Create simple copy, Create transformed copy, Create shape element copy, Refine shape, Attachment
- Preferences: Preferences, Fine tuning
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub