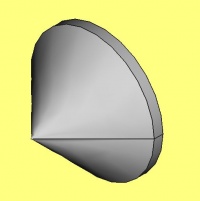
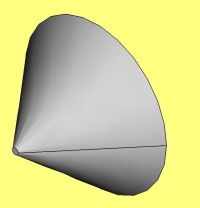
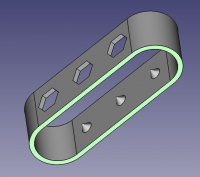
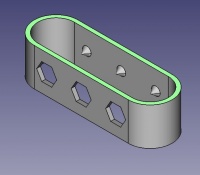
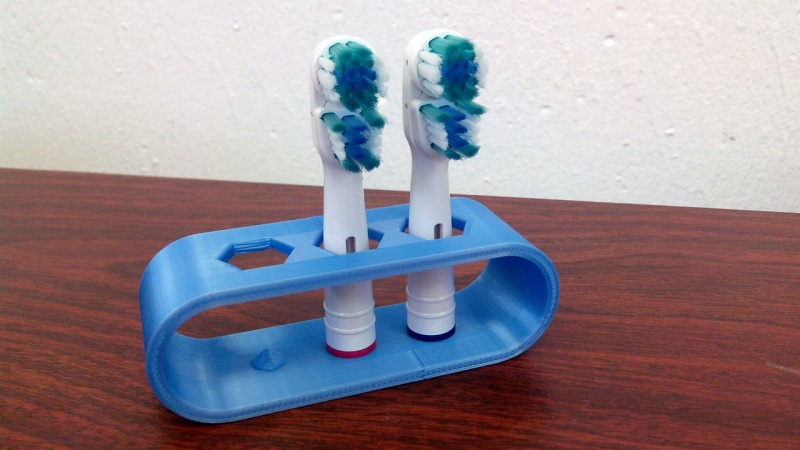
Soporte para la cabeza del cepillo de dientes
| Tema |
|---|
| Modeling |
| Nivel |
| Beginner |
| Tiempo para completar |
| 1 hour |
| Autores |
| EmmanuelG |
| Versión de FreeCAD |
| 0.16 or greater |
| Archivos de ejemplos |
| Thingiverse 2403310 |
| Ver también |
| None |
Un problema de la vida diaria
Los cepillos de dientes eléctricos rara vez vienen con un soporte para el cabezal, mientras que en una familia a menudo se ven varios cabezales utilizados con un solo cuerpo. Muchas personas que se enfrentan a un problema común nos llevan a una variedad de soluciones, como se puede ver en Thingiverse (200-800 proyectos están relacionados con eso). Aquí está la primera respuesta y cómo diseñarla.
Este tutorial le llevará a través de los pasos necesarios para modelar la pieza que se muestra en la imagen de abajo utilizando las herramientas básicas del Ambiente de trabajo DiseñoPiezas. (muchas de las herramientas y capacidades no están cubiertas).
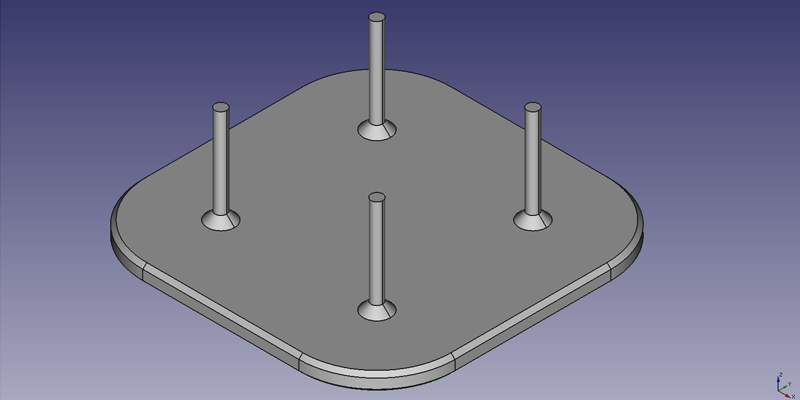
First idea : a plate
Primera idea : una placa
- Desde la página de inicio, seleccione
DiseñoPieza, o crea un nuevo documento y selecciona el ambiente de trabajo DiseñoPieza.
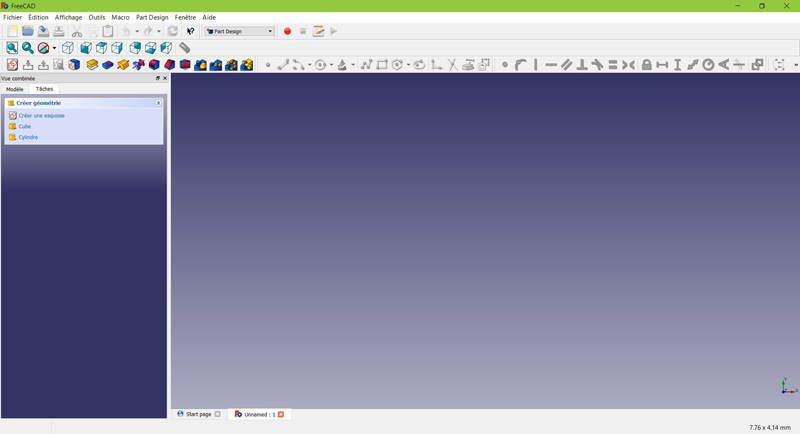

Create a sketch
Crear un croquis
- Haz clic en
Nuevo croquis. Ya sea desde el menú contextual de tareas de la izquierda, o desde la barra de herramientas de arriba o desde el menú Diseño Pieza de la parte superior.
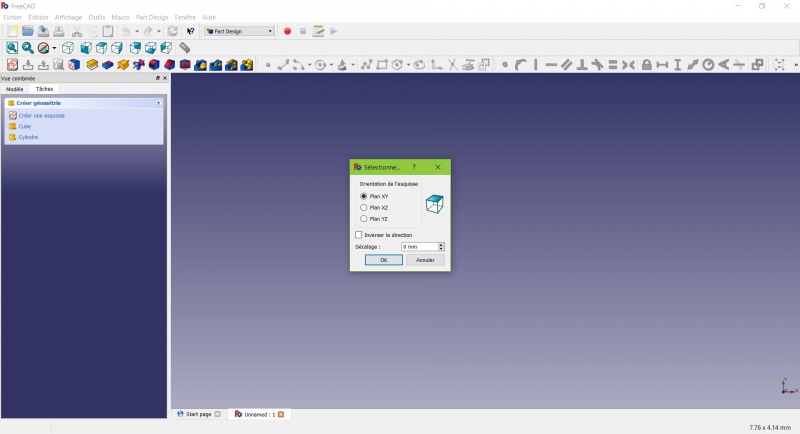

Un cuadro de diálogo le pide que elija la orientación del croquis y que proporcione un desplazamiento.
- Elegiremos el Plano XY como se muestra en la imagen de arriba (esa orientación corresponde a la placa de construcción común de la mayoría de las impresoras 3D), luego haz clic en OK.
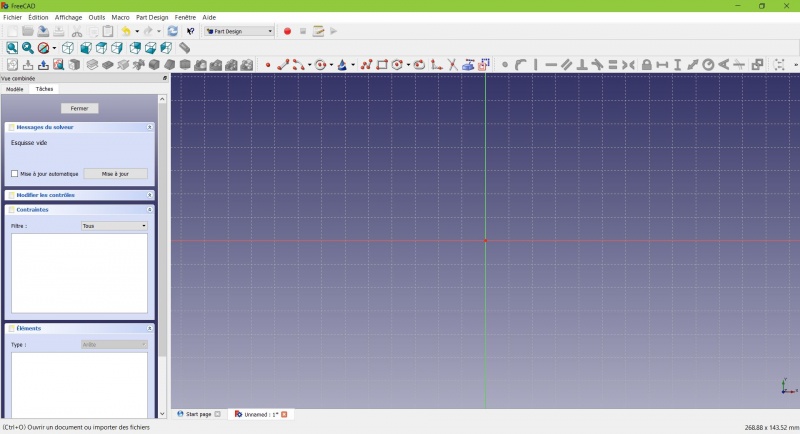
Ahora se encuentra frente al plano XY desde arriba, y tiene acceso a las herramientas de dibujo.
- Haz clic en
Rectangle.
- Haz clic para colocar un primer punto.
- Haz clic para colocar la esquina opuesta.
- Pulsa ESC o haz clic con el botón derecho del ratón para dejar de usar la herramienta.
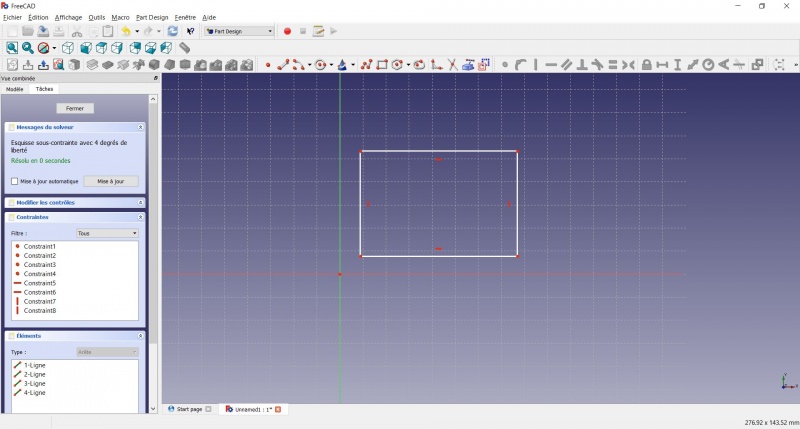
Ahora tiene un rectángulo flotante de dimensiones no especificadas.
- Haga clic en una línea del rectángulo, ahora tiene acceso a las herramientas de restricción a la derecha de la barra de herramientas (dependiendo del tamaño de su pantalla puede que tenga que arrastrarlas a la izquierda para verlas todas)
- Haga clic en
 Distancia
Distancia - Un diálogo le pide que establezca una dimensión. Insertar 80mm, haga clic en OK.
- Repite con el otro lado del rectángulo, también 80mm.
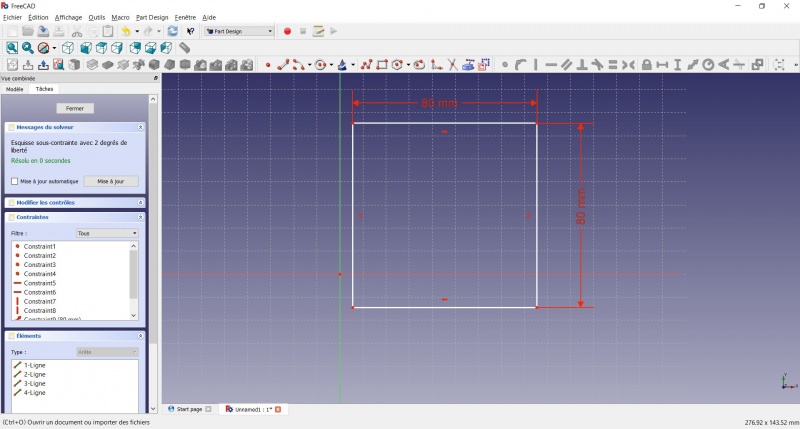
Ahora tienes un cuadrado flotante.
- Haga clic en el punto inferior izquierdo del cuadrado.
- Haga clic en el origen del plano XY (en la intersección de las dos líneas gruesas).
- Haga clic en
Coincidente.
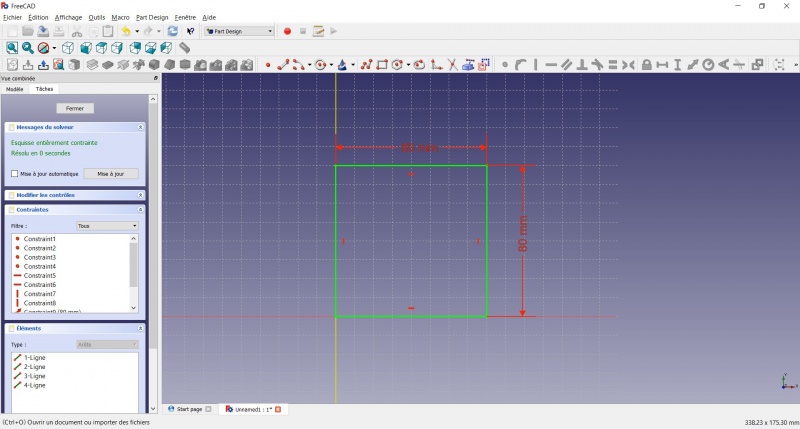
Ahora tiene un boceto totalmente restringido, como le indica el solucionador de la izquierda y el cambio de color. Es una buena práctica tener siempre un croquis totalmente restringido.
Un boceto poco restringido puede dejar espacio para cambios no deseados, si se modifica algo más tarde. Por el contrario, un croquis con demasiadas restricciones tampoco es bueno. En ese caso, el solucionador le advierte de las restricciones redundantes y debe eliminar algunas de ellas.
On the opposite, an over-constrained sketch is also not good. In that case the solver warn you of redundant constraints and you should remove some of them.
- To leave the sketch, click either on the "Close" button on the left, or the
 icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
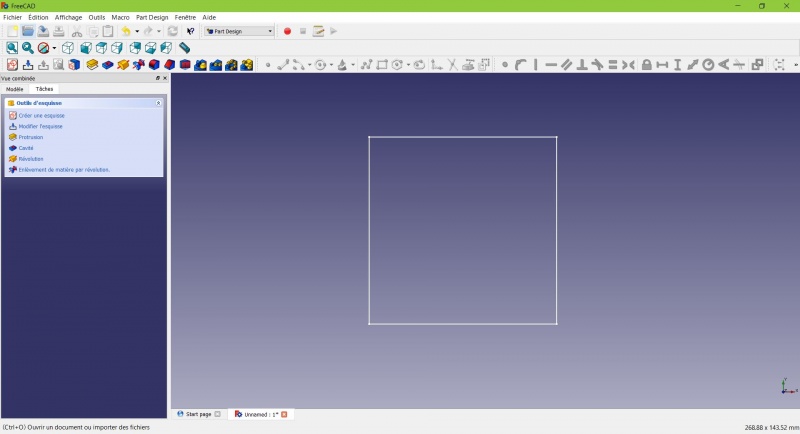
You now only see the square, and the contextual task menu on the left show you more options than before.
Create a pad
Crear una pastilla
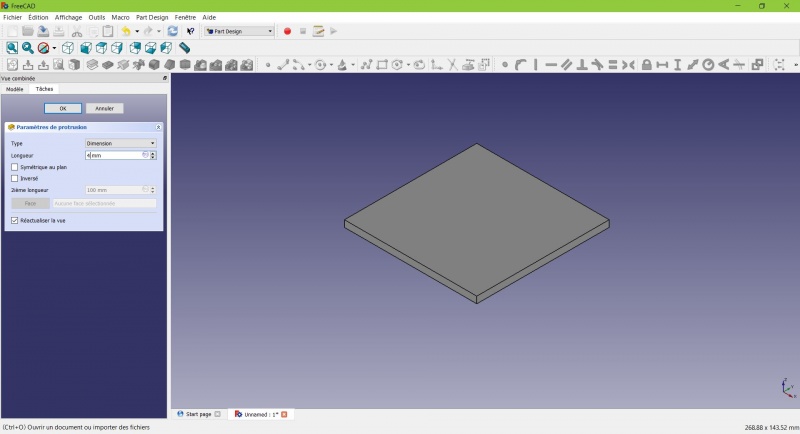
Your sketch is now in volume!
Create a sketch on it
Crear un croquis en él
- Selecciona la cara superior
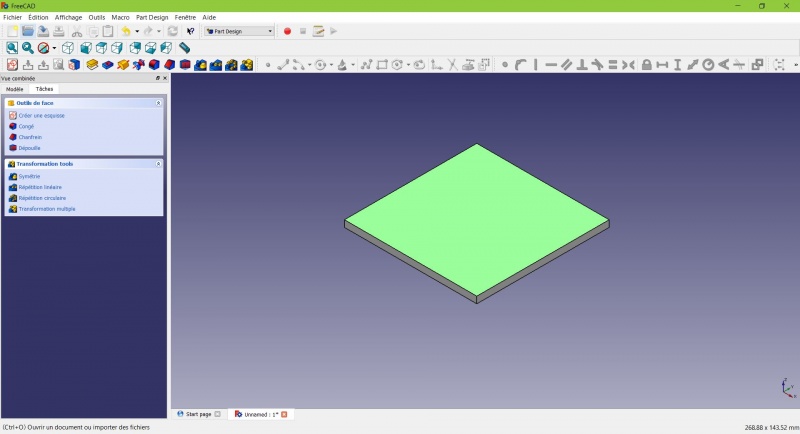
The color of the face change and you have more options in the contextual task menu.
- Click on
Circle, click to place the center, move the pointer and click to define the radius.
- Draw 4 circles on the pad (of any size)
- Press ESC or click the right mouse button to stop using the tool.
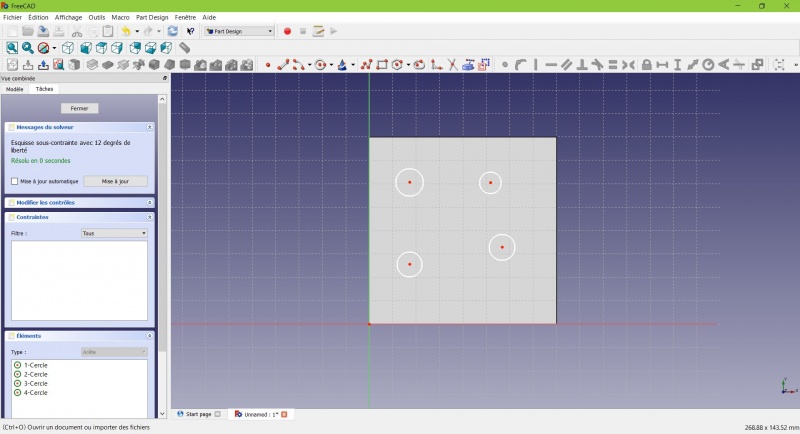
- Select the circles
- Click on
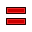 Equal Length
Equal Length
Now the circles share the same radius.
- Click on
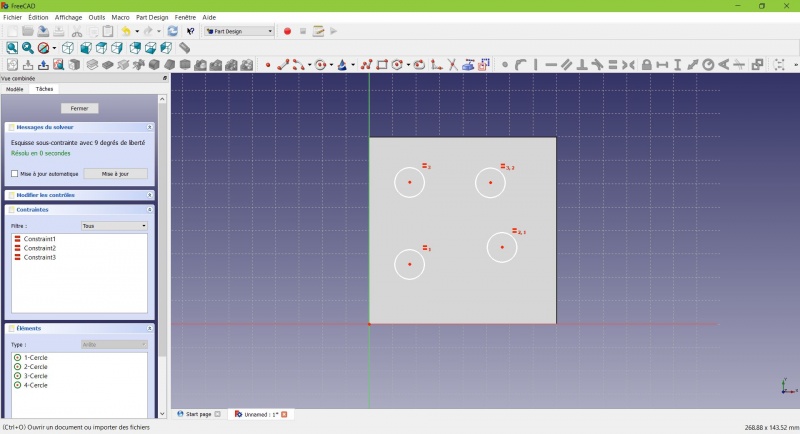
External geometry.
- Click on the four sides of the square, it add lines, color magenta.
Theses lines will serve as reference to position the circles.
- Click on
 Distance.
Distance. - Click on a center of a circle.
- Click on a magenta line.
- Set distance (20mm from each side).
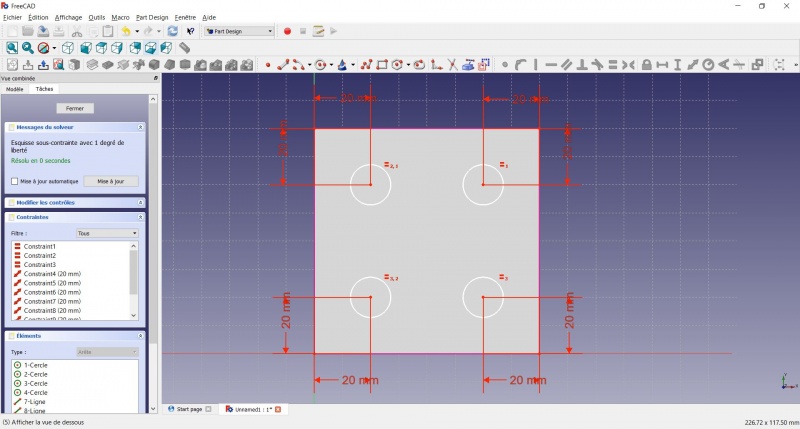
- Click on a circle
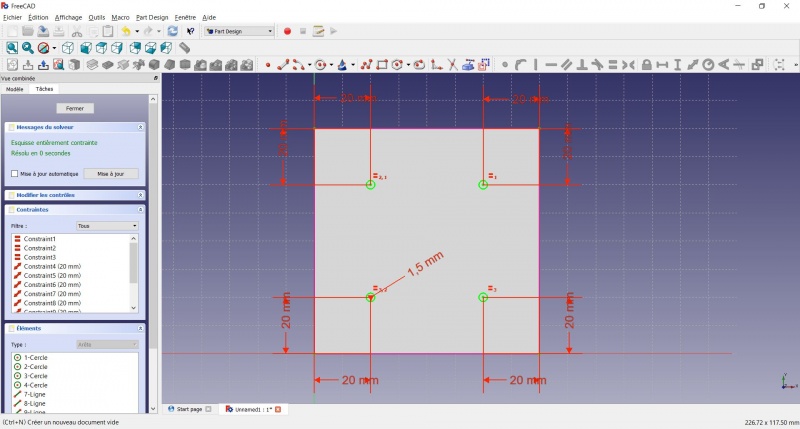
- Click on
Radius and set it at 1,5mm.
- To leave the sketch, click either on the "Close" button on the left, or the
 icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
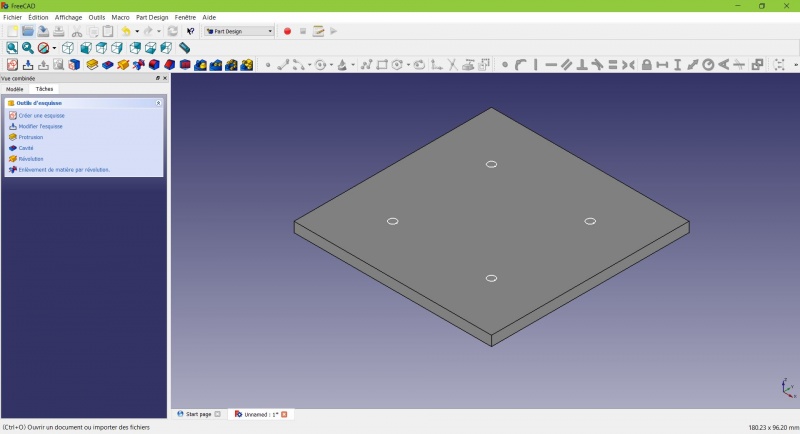
Create a pad
Crear una pastilla
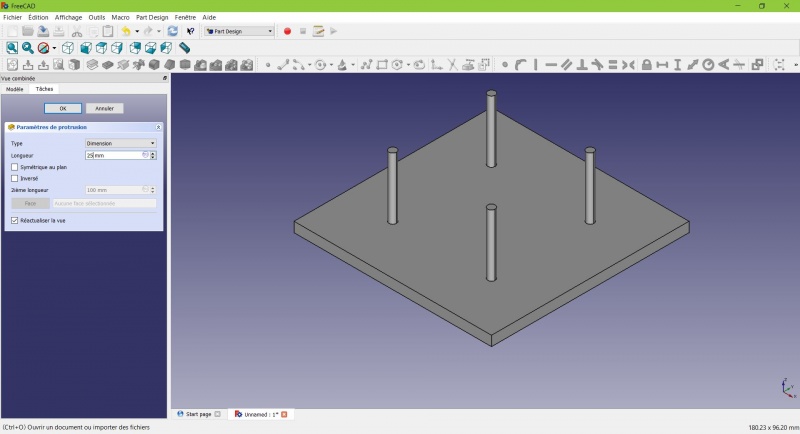
You have the basic shape, it just need final touches.
Rounding the corners
- Holding CTRL click on the vertical edge at each corner to select the four of them.
Don't hesitate to help you by switching the display mode (just at the left of the Axonometric View) between Wireframe and
Wireframe and shadow.
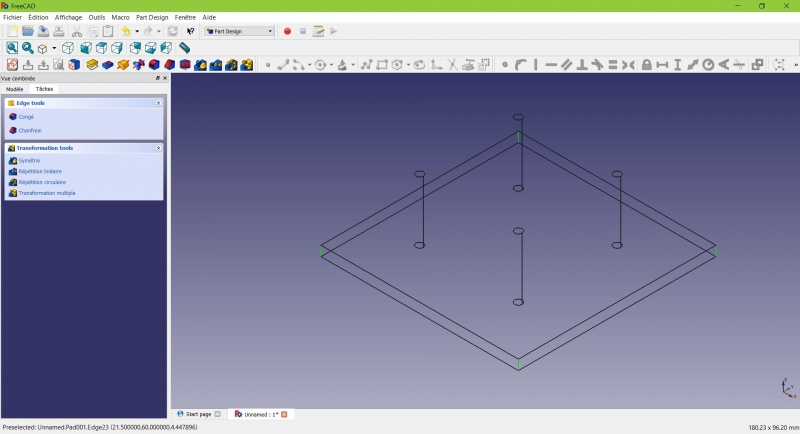
- Click on
Fillet.
- Set the radius at 20mm.
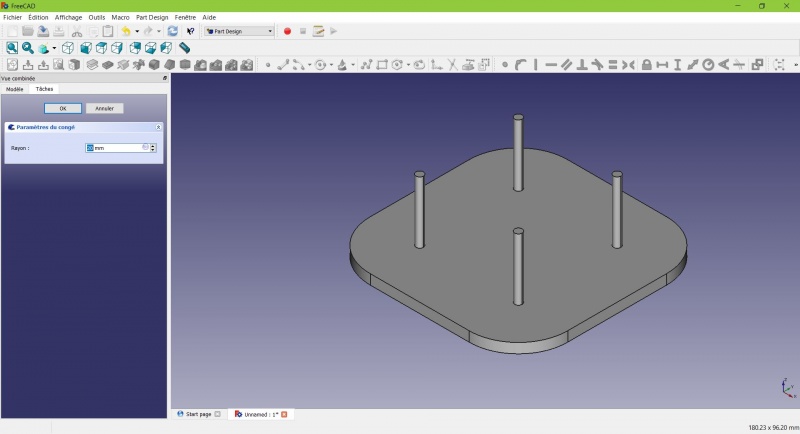
Much better.
Making it more robust
We need to add material at the base of the cylinders to make them less prone to snap. Because of the printing orientation these small surfaces will be fragile at the junction with the base.
- Select the circles at the base of the cylinders
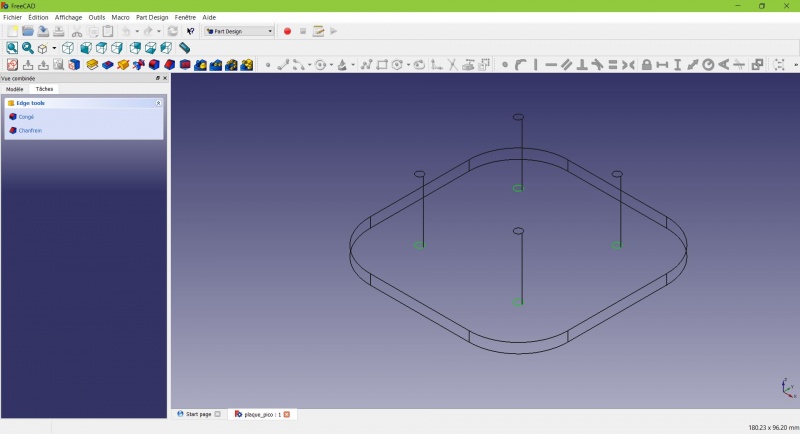
- Click on
Chamfer.
- Set it to 2mm.
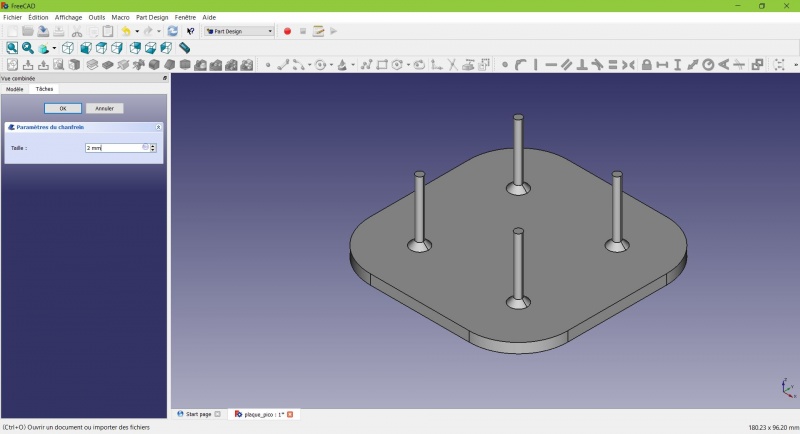
Chamfer the edges
The first layer of plastic is often being squashed a little too much, this will compensate that and save you time in cleaning the model. If the first layer is ok that will make it only nicer
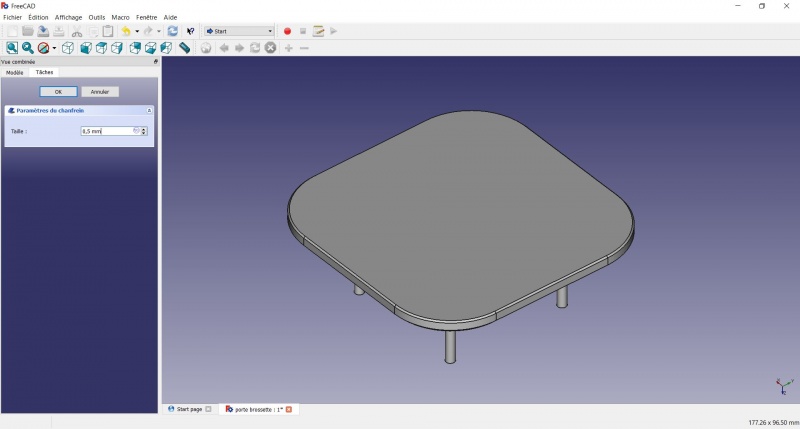
- Select the edges at the border of the upper face (holding CTRL ).
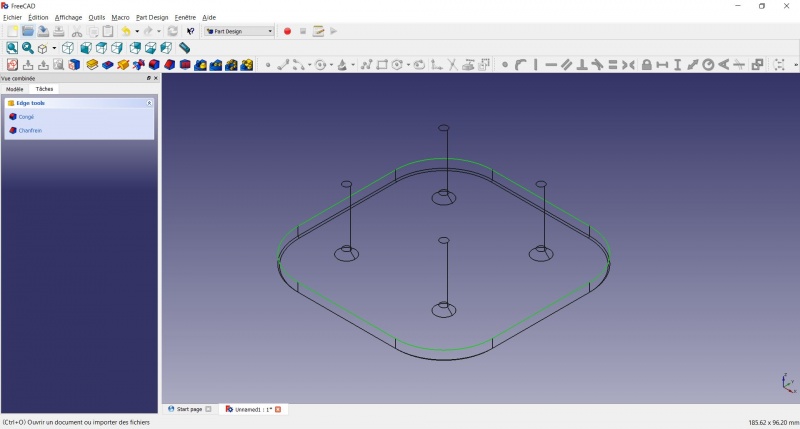
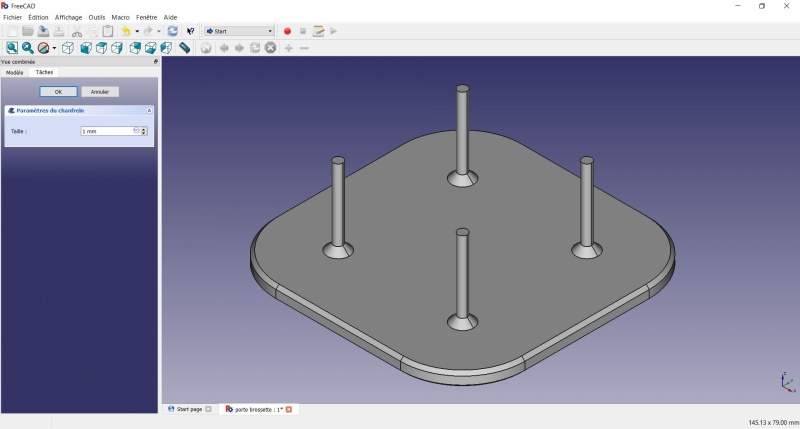
Tadaa!
Export as a .STL
- In the Combo View on the left, select the tree view instead of the contextual task menu, click on the last feature (the chamfer).
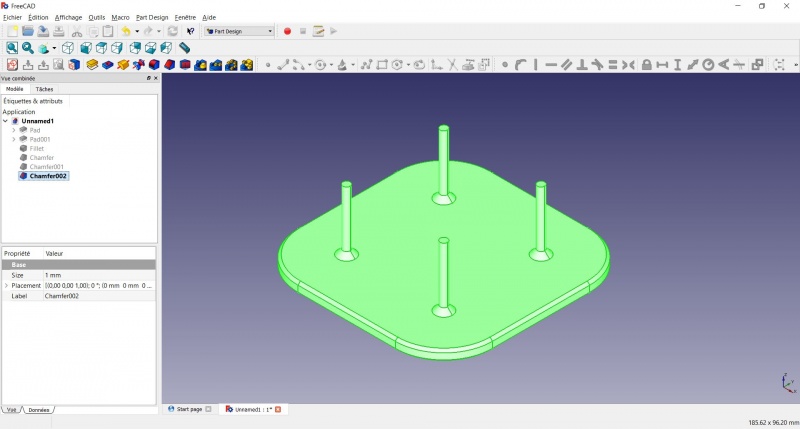
- Now you can select "Export..." from the File menu at the top left, and select the file format .STL.
- Just print it :-)
Inspiration
Inspiración
El modelo anterior es un buen punto de partida para utilizar FreeCAD, pero como soporte de cabezal de cepillo de dientes tiene sus defectos: debido a la orientación de la impresión y a la pequeña superficie los palos son propensos a romperse.
Inspired by the variety of solutions other people came up with, we will make this second version which will be much better.
Don't worry it is often needed to go through several revision for an idea (e.g. : once the prototype on the picture was used, we added more space between the heads so that they should not touch).
In this second part you will also learn to use more tools, like the powerful Linear repetition.
Second idea : a band
Create a sketch

- Draw a
Slot
- Click to place the first center
- Move to define the length and radius
- Click to set the second center.
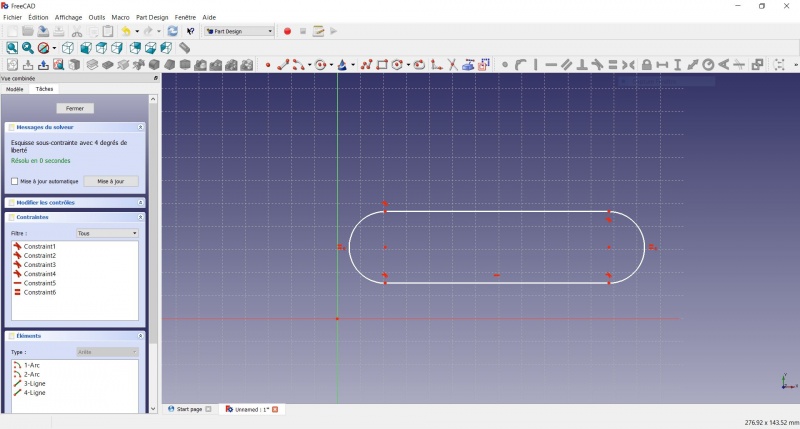
You now have a floating slot of unspecified dimensions.
- Click on one of the horizontal lines of the slot
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 75mm, click OK.
- that's for a 3 head stand, count 25mm for each, if you want more
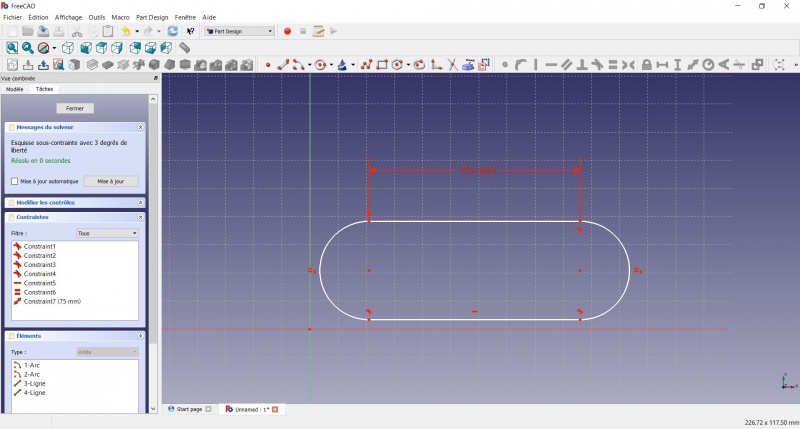
- Click on one point of the horizontal line
- Click on one point of the other horizontal line
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 29mm, click OK.
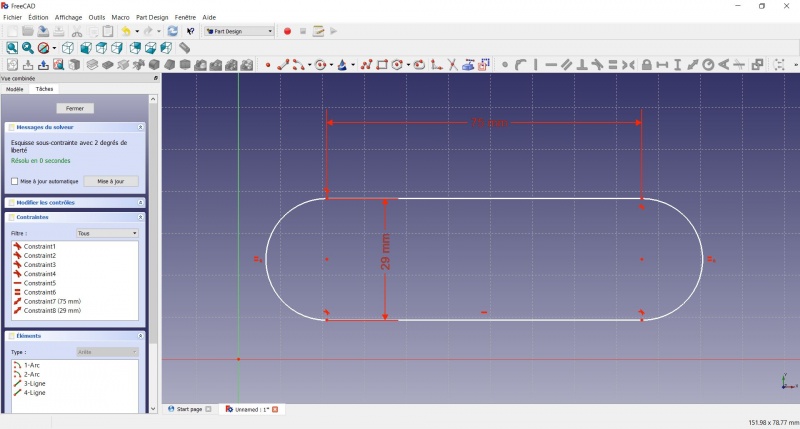
- Draw a
Slot around the first slot.
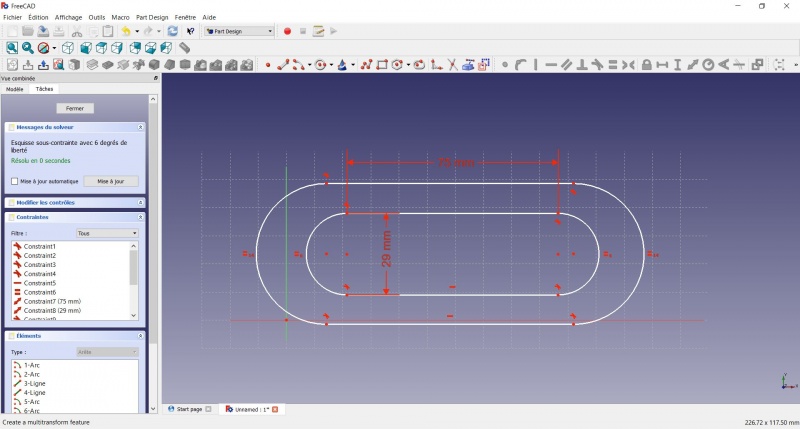
- Make the centers of the second slot coincident with the centers of the first slot with
Coincident.
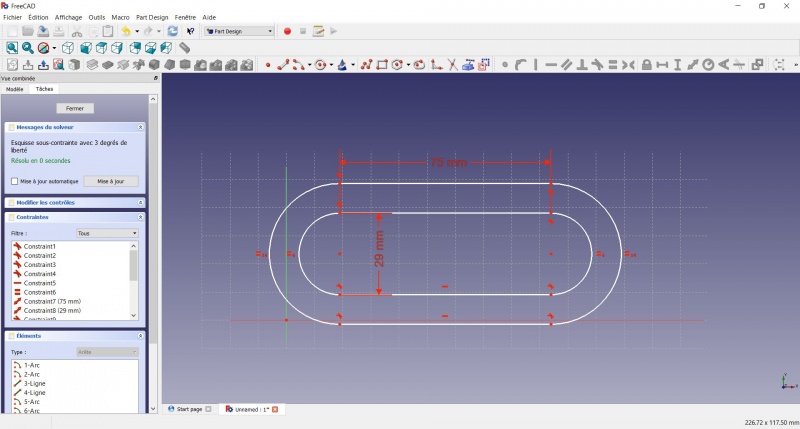
- Click on one point of the horizontal line of the first slot
- Click on one point of the nearest horizontal line of the second slot
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 3mm, click OK.
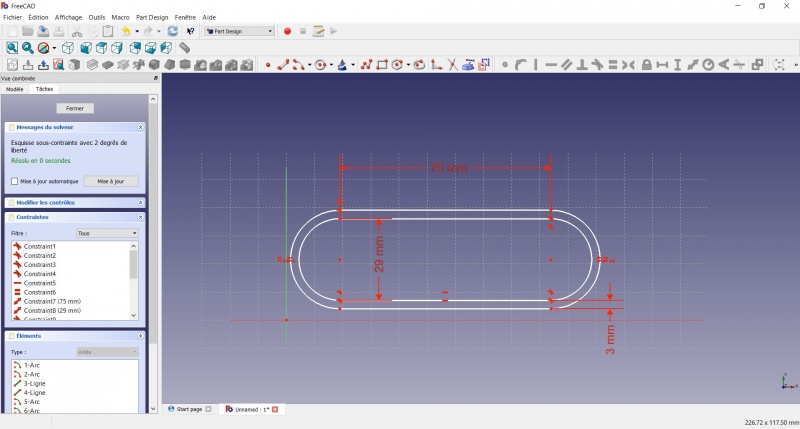
- To make the sketch fully constrained
- Click on the lower left point of the second slot
- Click on the origin of the XY plan
- Click on
Coincident
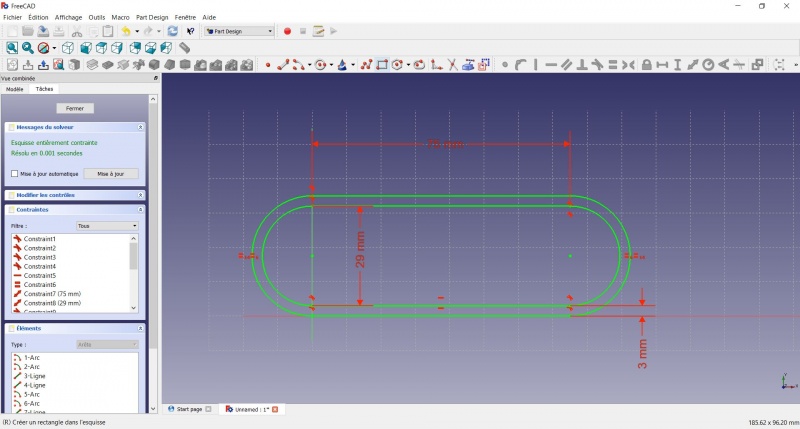
- To leave the sketch, click either on the "Close" button on the left, or the
 icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
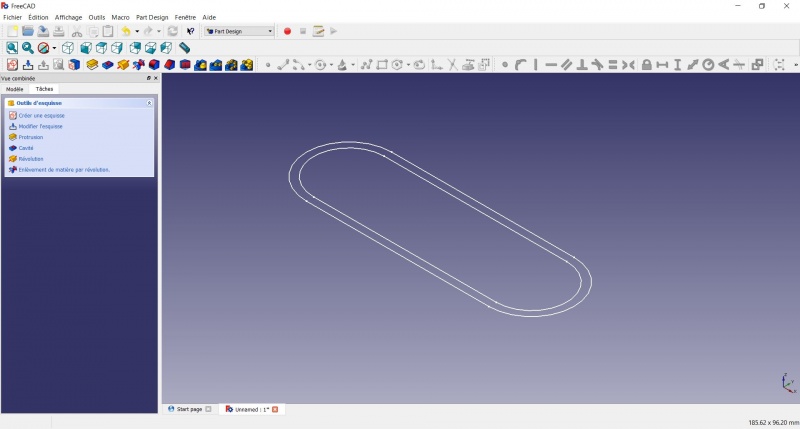
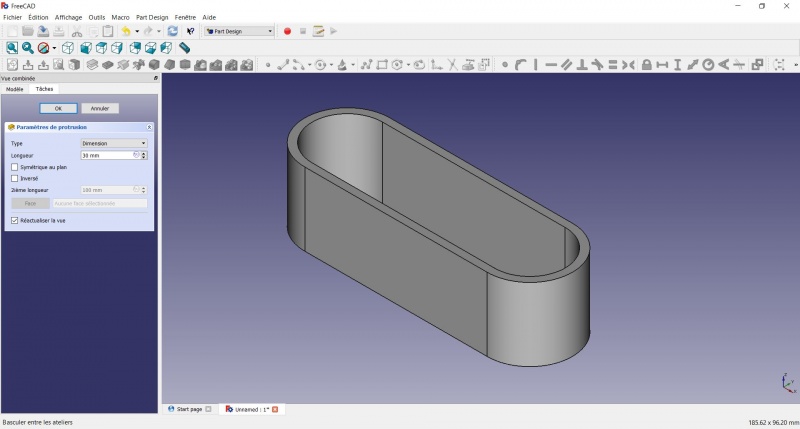
Create a pad
- Click on
Axonometric among the standard views, to better see what will happen.
- Click on
Pad.
- Enter 30mm and click OK.
Create a sketch on it
- Select the upper face
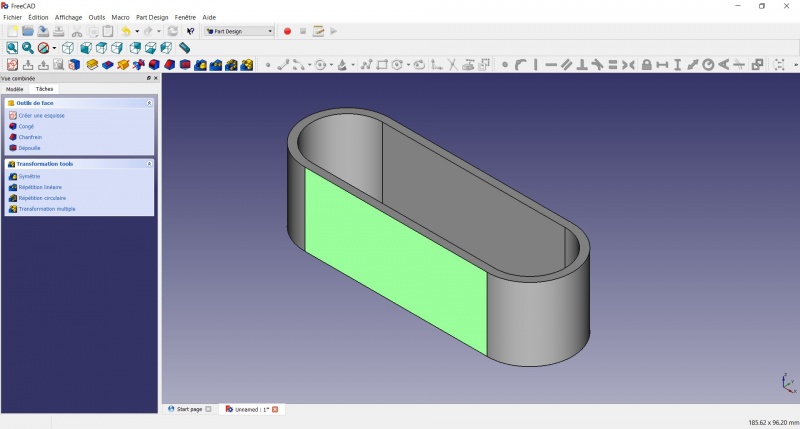
- Draw an
Hexagon
- Click to place the center
- Move to define the radius
- Click to set
- Click on an edge of the hexagon
- Click on
Horizontal
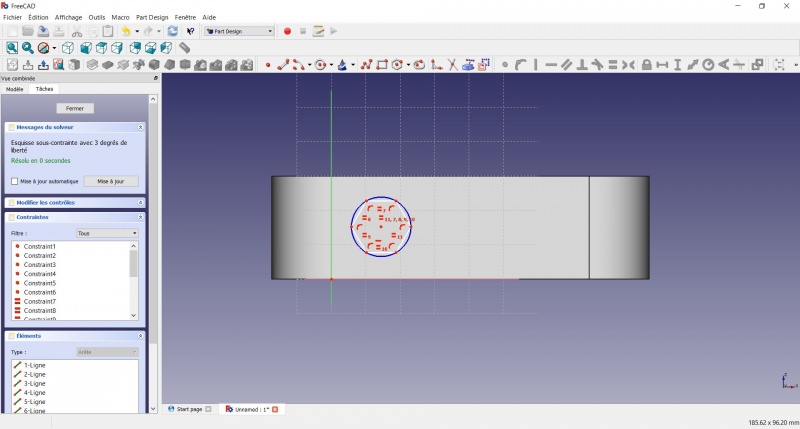
- Click on the center of the hexagon
- Click on the horizontal line of the XY plane
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 15mm, click OK.
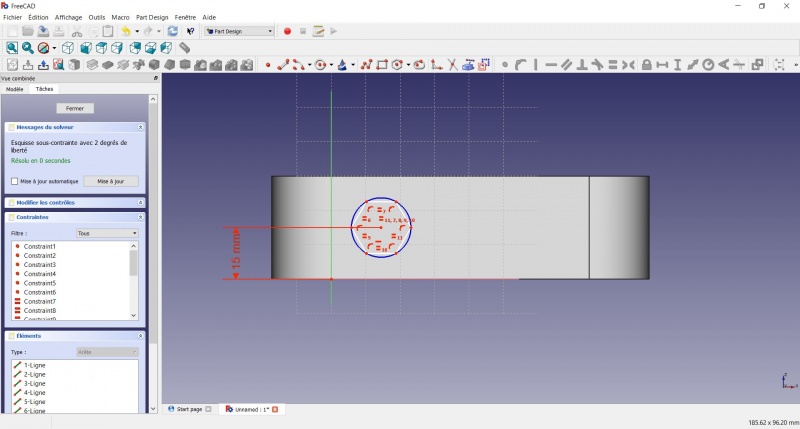
- Click on the center of the hexagon
- Click on the vertical of the XY plane
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 10mm, click OK.
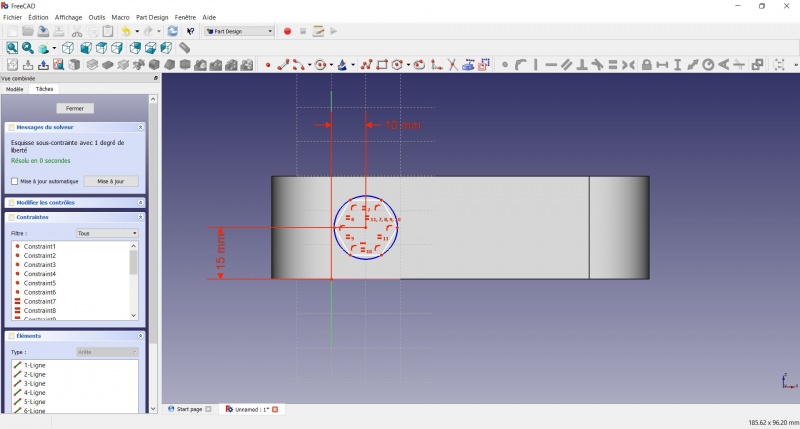
- Click on the blue circle of the hexagon
- Click on
Radius
- A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 8mm, click OK.
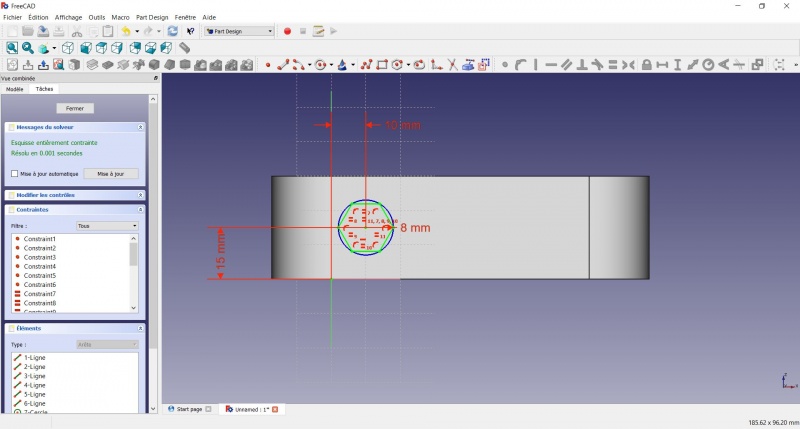
- To leave the sketch, click either on the "Close" button on the left, or the
 icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
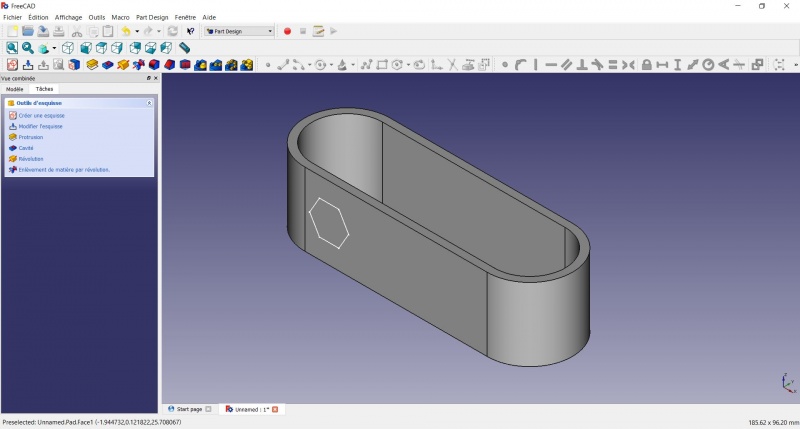
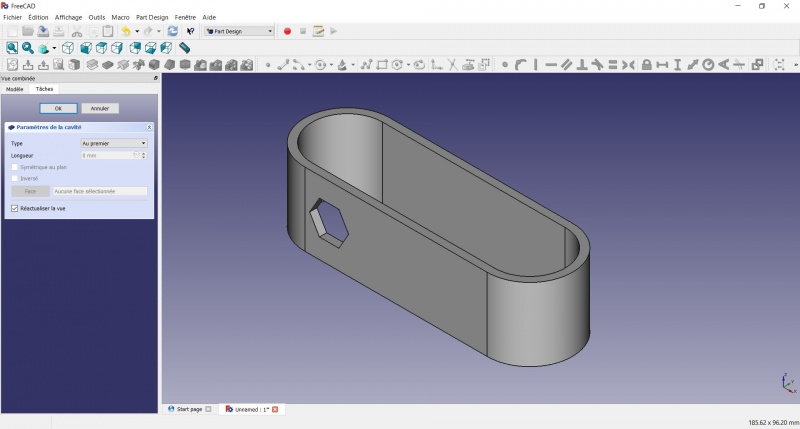
Create a hole
- Click on
Axonometric among the standard views, to better see what will happen.
- Click on
Pocket.
- Select to the first in the dropdown menu and click OK.
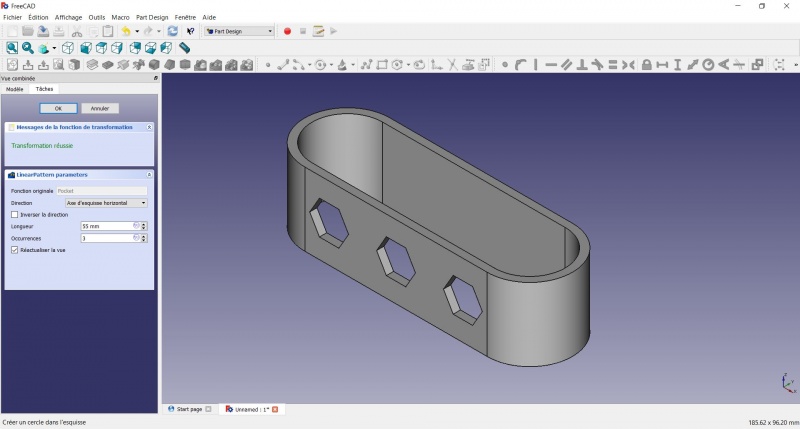
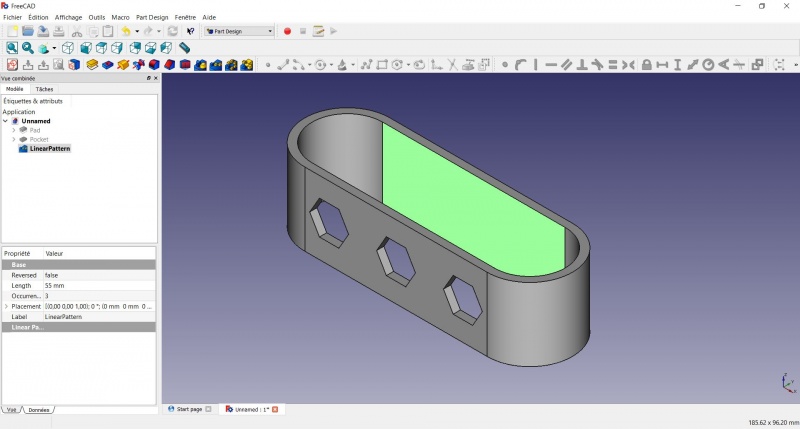
Linear repetition
- In the Combo View on the left, select the tree view instead of the contextual task menu, click on the pocket feature.
- Click on
LinearPattern.
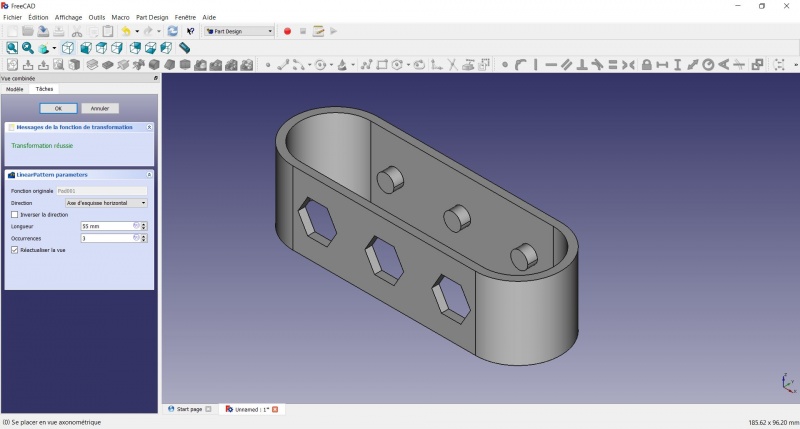
- Set the length at 55mm and occurencies at 3, then click OK.
Create a sketch on it
- Select the inner face
- Click on
Circle, click to place the center, move the pointer and click to define the radius.
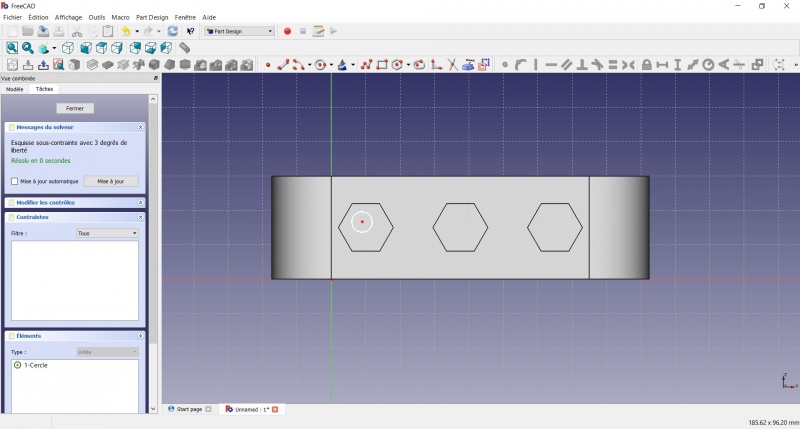
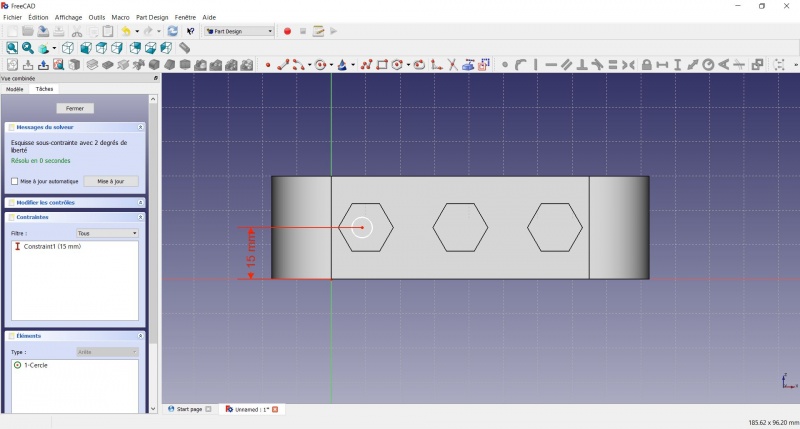
- Click on the center of the circle
- Click on the horizontal line of the XY plane
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 15mm, click OK.
- Click on the center of the circle
- Click on the vertical of the XY plane
- Click on
 Distance
Distance - A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 10mm, click OK.
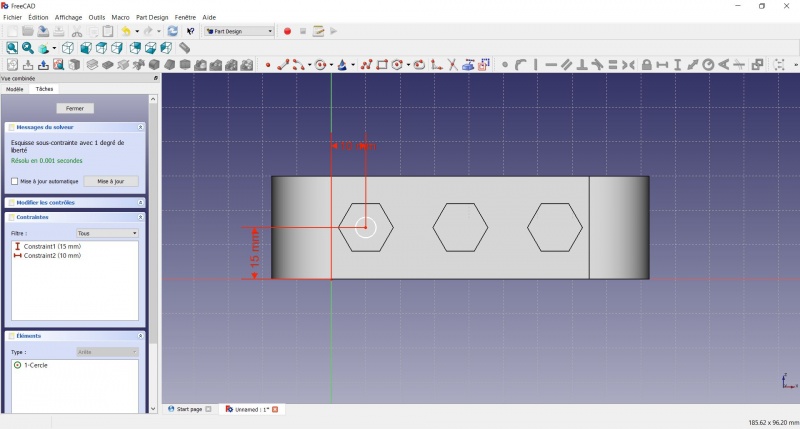
- Click on the circle
- Click on
Radius
- A dialog prompts you to set a dimension. Enter 3.5mm, click OK.
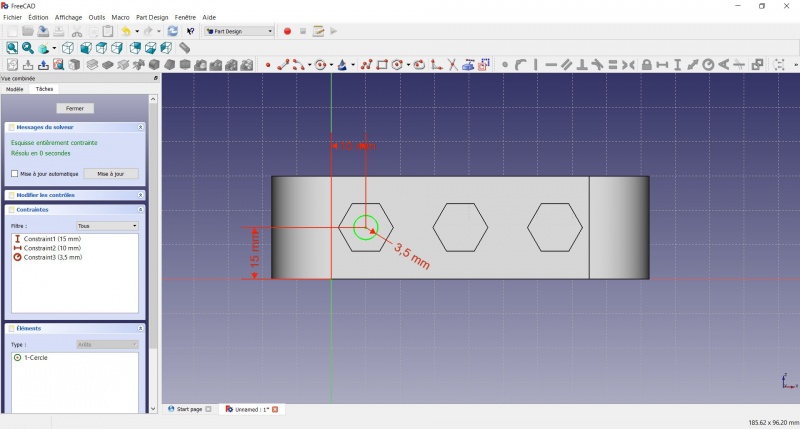
- To leave the sketch, click either on the "Close" button on the left, or the
 icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
icon in the toolbar, or press ESC.
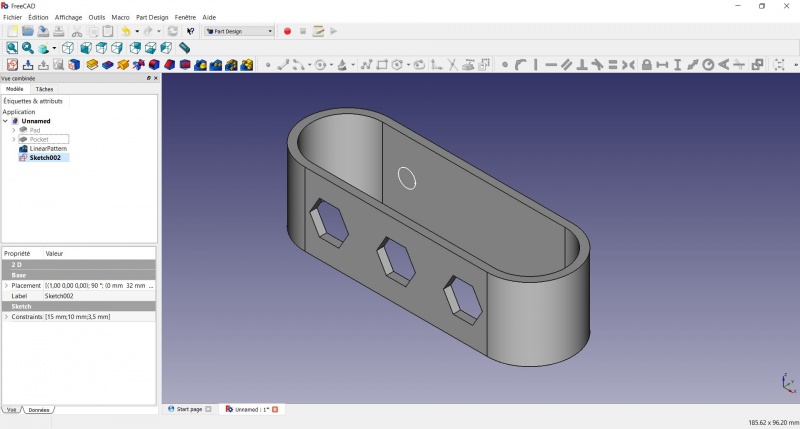
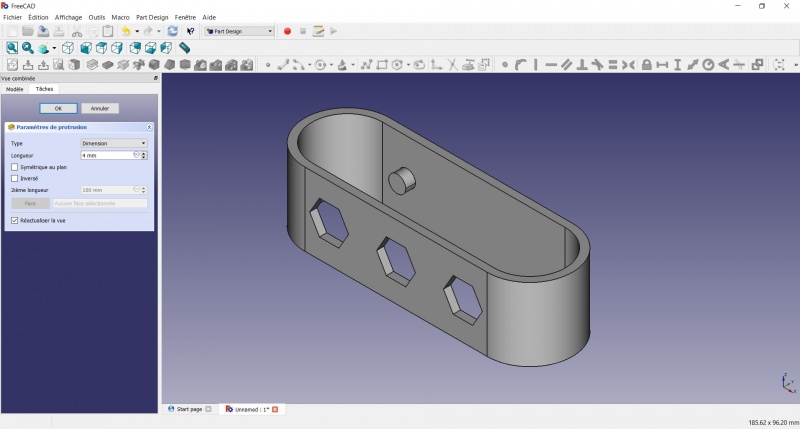
Create a pad
Crear una pastilla
- Haz clic en
Axonométrico entre las vistas estándar, para ver mejor lo que ocurrirá.
- Haga clic en
Pastilla.
- Insertar 4mm y haga clic en OK.

Linear repetition
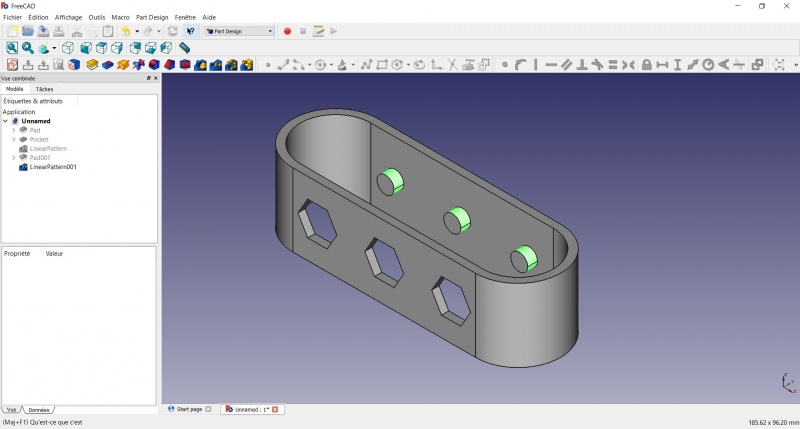
- In the Combo View on the left, select the tree view instead of the contextual task menu, click on the pad feature.
- Click on
LinearPattern.
- Set the length at 55mm and occurencies at 3, then click OK.
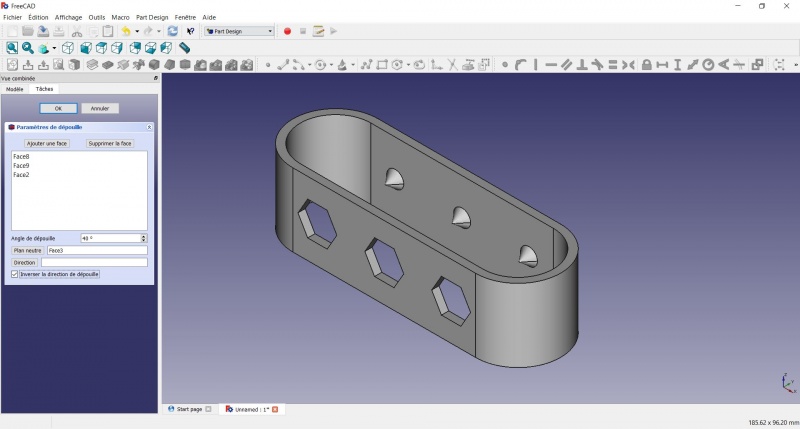
Draft
- Select the side of each round pads
- Click on
Draft.
- Set the draft angle at 40°.
- Click on "Neutral plane" and select the face on which the sketch is drawn.
- Tick "Invert the draft direction".
We could have used a chamfer to do something similar, but the draft is more appropriate in this case.
Chamfer = left / Draft = right
Finishes
- Holding CTRL select the bottom and top faces.
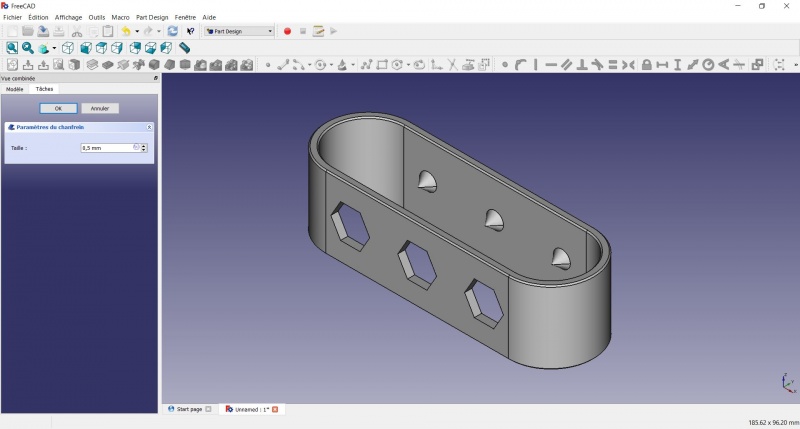
Perfect!
Export as a .STL
- In the Combo View on the left, select the tree view instead of the contextual task menu, click on the last feature (the chamfer).
- Now you can select "Export..." from the File menu at the top left, and select the file format .STL.
- Print it instead of the first version or to replace it if it eventually broke ;-)
- Structure tools: Part, Group
- Helper tools: Create body, Create sketch, Attach sketch, Edit sketch, Validate sketch, Check geometry, Create a shape binder, Create a sub-object(s) shape binder, Create a clone, Create a datum plane, Create a datum line, Create a datum point, Create a local coordinate system
- Modeling tools:
- Additive tools: Pad, Revolution, Additive loft, Additive pipe, Additive helix, Additive box, Additive cylinder, Additive sphere, Additive cone, Additive ellipsoid, Additive torus, Additive prism, Additive wedge
- Subtractive tools: Pocket, Hole, Groove, Subtractive loft, Subtractive pipe, Subtractive helix, Subtractive box, Subtractive cylinder, Subtractive sphere, Subtractive cone, Subtractive ellipsoid, Subtractive torus, Subtractive prism, Subtractive wedge
- Boolean: Boolean operation
- Dress-up tools: Fillet, Chamfer, Draft, Thickness
- Transformation tools: Mirrored, Linear Pattern, Polar Pattern, Create MultiTransform, Scaled
- Extras: Sprocket, Involute gear, Shaft design wizard
- Context menu: Set tip, Move object to other body, Move object after other object, Appearance, Color per face
- Preferences: Preferences, Fine tuning
- General: Create sketch, Edit sketch, Attach sketch, Reorient sketch, Validate sketch, Merge sketches, Mirror sketch, Leave sketch, View sketch, View section, Toggle grid, Toggle snap, Configure rendering order, Stop operation
- Sketcher geometries: Point, Polyline, Line, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Arc of ellipse, Arc of hyperbola, Arc of parabola, Circle, Circle by 3 points, Ellipse, Ellipse by 3 points, Rectangle, Centered rectangle, Rounded rectangle, Triangle, Square, Pentagon, Hexagon, Heptagon, Octagon, Regular polygon, Slot, Arc slot, B-spline by control points, Periodic B-spline by control points, B-spline by knots, Periodic B-spline by knots, Toggle construction geometry
- Sketcher constraints:
- Dimensional constraints: Dimension, Horizontal distance, Vertical distance, Distance, Auto radius/diameter, Radius, Diameter, Angle, Lock
- Geometric constraints: Coincident (unified), Coincident, Point on object, Horizontal/vertical, Horizontal, Vertical, Parallel, Perpendicular, Tangent or collinear, Equal, Symmetric, Block
- Other constraints: Refraction (Snell's law)
- Constraint tools: Toggle driving/reference constraint, Activate/deactivate constraint
- Sketcher tools: Fillet, Chamfer, Trim, Split, Extend, External geometry, Carbon copy, Select origin, Select horizontal axis, Select vertical axis, Array transform, Polar transform, Scale transform, Offset geometry, Symmetry, Remove axes alignment, Delete all geometry, Delete all constraints
- Sketcher B-spline tools: Convert geometry to B-spline, Increase B-spline degree, Decrease B-spline degree, Increase knot multiplicity, Decrease knot multiplicity, Insert knot, Join curves
- Sketcher visual: Select unconstrained DoF, Select associated constraints, Select associated geometry, Select redundant constraints, Select conflicting constraints, Show/hide circular helper for arcs, Show/hide B-spline degree, Show/hide B-spline control polygon, Show/hide B-spline curvature comb, Show/hide B-spline knot multiplicity, Show/hide B-spline control point weight, Show/hide internal geometry, Switch virtual space
- Additional: Sketcher Dialog, Preferences, Sketcher scripting
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub