Draft WorkingPlaneProxy
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Utilities → Create working plane proxy Utils → Create working plane proxy |
| Workbenches |
| Draft, BIM |
| Default shortcut |
| None |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| Draft SelectPlane |
Description
The Draft WorkingPlaneProxy command creates a working plane proxy to save the current Draft working plane. A working plane proxy can be used to quickly restore a working plane. The camera position and visibility of the objects in the 3D view are also saved in the working plane proxy and can, optionally, be restored as well.
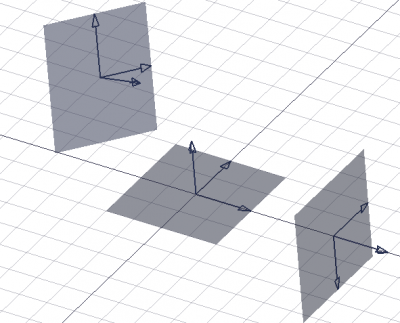
Three working plane proxies showing different orientations and offsets
Usage
- Optionally change the working plane.
- Optionally change the 3D view.
- Optionally change the visibility state of objects in the document.
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- Draft: Press the
Create working plane proxy button.
- Draft: Select the Utilities →
Create working plane proxy option from the menu, or from the Tree view or 3D view context menu.
- BIM: Select the Utils →
Create working plane proxy option from the menu.
- Draft: Press the
- A working plane proxy is created.
- To align the working plane with a working plane proxy, double-click the working plane proxy in the Tree view or use it with the Draft SelectPlane command.
For a Draft WorkingPlaneProxy these additional options are available in the Tree view context menu:
Write camera position: updates the ViewView Data property of the working plane proxy with the current 3D view camera settings.
Write objects state: updates the ViewVisibility Map property of the working plane proxy with the current visibility state of objects in the document.
Notes
- Working plane proxies can be moved and rotated like any other object. Use
Draft Snap Center to snap to their DataPlacement point.
Properties
See also: Property editor.
A Draft WorkingPlaneProxy object is derived from an App FeaturePython object and inherits all its properties. It also has the following additional properties:
Data
Base
- DataPlacement (
Placement): specifies the position of the working plane proxy in the 3D view. See Placement. - Data (Hidden)Shape (
Shape): specifies the shape of the working plane proxy.
View
Base
- ViewLine Color (
Color): specifies the color of all elements of the working plane proxy. - ViewLine Width (
Float): specifies the line width of the axes and arrow symbols. - ViewRestore State (
Bool): specifies if the ViewVisibility Map is restored when the working plane is aligned with the working plane proxy. - ViewRestore View (
Bool): specifies if the ViewView Data is restored when the working plane is aligned with the working plane proxy. - ViewTransparency (
Percent): specifies the transparency of the face of the working plane proxy. - ViewView Data (
FloatList): specifies the camera position and settings. - View (Hidden)Visibility Map (
Map): specifies the visibility state of objects.
Draft
- ViewArrow Size (
Length): specifies the size of the arrow symbols displayed at the tip of the three axes. - ViewDisplay Size (
Length): specifies the length and width of the working plane proxy.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
To create a Draft WorkingPlaneProxy use the make_workingplaneproxy method of the Draft module.
If the Draft Workbench is active the FreeCAD application object has a DraftWorkingPlane property which stores the current working plane. The Placement from the getPlacement method of the DraftWorkingPlane object can be used to create an aligned working plane proxy. The Placement of a working plane proxy in turn can be used to realign the working plane.
# This code only works if the Draft Workbench is active!
import FreeCAD as App
import FreeCADGui as Gui
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
workplane = App.DraftWorkingPlane
place = workplane.getPlacement()
proxy = Draft.make_workingplaneproxy(place)
proxy.ViewObject.DisplaySize = 3000
proxy.ViewObject.ArrowSize = 200
axis2 = App.Vector(1, 1, 1)
point2 = App.Vector(3000, 0, 0)
place2 = App.Placement(point2, App.Rotation(axis2, 90))
proxy2 = Draft.make_workingplaneproxy(place2)
proxy2.ViewObject.DisplaySize = 3000
proxy2.ViewObject.ArrowSize = 200
workplane.setFromPlacement(proxy2.Placement, rebase=True)
Gui.Snapper.setGrid()
doc.recompute()
- Drafting: Line, Polyline, Fillet, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Ellipse, Rectangle, Polygon, B-spline, Cubic Bézier curve, Bézier curve, Point, Facebinder, ShapeString, Hatch
- Annotation: Text, Dimension, Label, Annotation styles, Annotation scale
- Modification: Move, Rotate, Scale, Mirror, Offset, Trimex, Stretch, Clone, Array, Polar array, Circular array, Path array, Path link array, Point array, Point link array, Edit, Subelement highlight, Join, Split, Upgrade, Downgrade, Wire to B-spline, Draft to sketch, Set slope, Flip dimension, Shape 2D view
- Draft Tray: Select plane, Set style, Toggle construction mode, AutoGroup
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid
- Miscellaneous: Apply current style, Layer, Manage layers, Add a new named group, Move to group, Select group, Add to construction group, Toggle normal/wireframe display, Create working plane proxy, Heal, Show snap toolbar
- Additional: Constraining, Pattern, Preferences, Import Export Preferences, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Context menu:
- Layer container: Merge layer duplicates, Add new layer
- Layer: Activate this layer, Select layer contents
- Text: Open hyperlinks
- Wire: Flatten
- Working plane proxy: Write camera position, Write objects state
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub