Draft Hatch
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| Drafting → Hatch Annotation → Hatch |
| Workbenches |
| Draft, BIM |
| Default shortcut |
| H A |
| Introduced in version |
| 0.20 |
| See also |
| Draft Pattern |
Description
The Draft Hatch command creates hatches on the planar faces of a selected object.
Usage
- Select an object with faces. Only the planar faces of the object will be hatched.
- There are several ways to invoke the command:
- The Hatch task panel opens. See Options for more information.
- Press the OK button to finish the command.
Options
- Press the ... button to select a PAT file. See Notes.
- Select a Pattern from the file. It is currently advisable to avoid patterns with dashed lines.
- Specify a Scale for the pattern.
- Specify a Rotation for the pattern.
- Press Esc or the Cancel button to abort the command.
Pattern alignment
When the hatch pattern for a face is calculated it is temporarily translated to the global XY plane by default. For a face with straight edges the first straight edge determines how this happens. The first point of that edge is put on the origin, and the edge itself is aligned with the X-axis. If you create Draft Wires with that in mind you can control how the hatch pattern is aligned with the outline of the face.
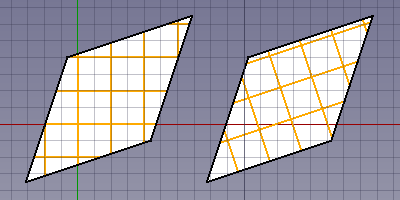
If all faces of the selected object are on the global XY plane you can switch off this default behavior by setting the DataTranslate property of the Draft Hatch to false. The hatch pattern is then aligned with the origin and the X axis of the global coordinate system. For faces on the XY plane with straight edges the DataTranslate property can be used to switch between absolute (on the left in the image) and relative (on the right in the image) patterns.
Two Draft Wires with hatches.
The wires were created in a CCW direction starting from the bottom left point.
For the Draft Hatch on the left the Translate property is set to false.
For the Draft Hatch on the right it is set to true.
Notes
- For now the advice is to download a PAT file. Many can be found online. You can for example do a web search for acad.pat or acadiso.pat.
- A small PAT file is installed with FreeCAD: <program_folder>/data/Mod/TechDraw/PAT/FCPAT.pat, where <program_folder> is the FreeCAD program folder:
- On Linux it is usually /usr/share/freecad.
- On Windows it is usually C:\Program Files\FreeCAD.
- On macOS it is usually /Applications/FreeCAD.
Preferences
See also: Preferences Editor and Draft Preferences.
The following preferences are involved:
- PAT file: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → TechDraw → PAT → FilePattern.
- Pattern: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → TechDraw → PAT → NamePattern.
- Scale: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Draft → HatchPatternScale.
- Rotation: Tools → Edit parameters... → BaseApp → Preferences → Mod → Draft → HatchPatternRotation.
Properties
See also: Property editor.
A Draft Hatch object is derived from a Part Feature object and inherits all its properties. It also has the following additional properties:
Data
Hatch
- DataBase (
Link): specifies the object whose faces are hatched. - DataFile (
File): specifies the PAT file. - DataPattern (
String): specifies the pattern name. - DataRotation (
Angle): specifies the rotation of the pattern. - DataScale (
Float): specifies the scale of the pattern. - DataTranslate (
Bool): specifies if the faces are temporarily translated to the global XY plane during the hatching process. Setting it tofalsemay give wrong results for non-XY faces.
Scripting
See also: Autogenerated API documentation and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
To create a Draft Hatch use the make_hatch method of the Draft module.
hatch = make_hatch(baseobject, filename, pattern, scale, rotation)
Example:
import FreeCAD as App
import Draft
doc = App.newDocument()
rectangle = Draft.make_rectangle(4000, 1000)
rectangle.MakeFace = True
filename = App.getHomePath() + "data/Mod/TechDraw/PAT/FCPAT.pat"
pattern = "Horizontal5"
hatch = Draft.make_hatch(rectangle, filename, pattern, scale=50, rotation=45)
doc.recompute()
- Drafting: Line, Polyline, Fillet, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Circle, Ellipse, Rectangle, Polygon, B-spline, Cubic Bézier curve, Bézier curve, Point, Facebinder, ShapeString, Hatch
- Annotation: Text, Dimension, Label, Annotation styles, Annotation scale
- Modification: Move, Rotate, Scale, Mirror, Offset, Trimex, Stretch, Clone, Array, Polar array, Circular array, Path array, Path link array, Point array, Point link array, Edit, Subelement highlight, Join, Split, Upgrade, Downgrade, Wire to B-spline, Draft to sketch, Set slope, Flip dimension, Shape 2D view
- Draft Tray: Select plane, Set style, Toggle construction mode, AutoGroup
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid
- Miscellaneous: Apply current style, Layer, Manage layers, Add a new named group, Move to group, Select group, Add to construction group, Toggle normal/wireframe display, Create working plane proxy, Heal, Show snap toolbar
- Additional: Constraining, Pattern, Preferences, Import Export Preferences, DXF/DWG, SVG, OCA, DAT
- Context menu:
- Layer container: Merge layer duplicates, Add new layer
- Layer: Activate this layer, Select layer contents
- Text: Open hyperlinks
- Wire: Flatten
- Working plane proxy: Write camera position, Write objects state
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub