Arch Stairs
This page has been updated for that version.
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| 3D/BIM → Stairs |
| Workbenches |
| BIM |
| Default shortcut |
| S R |
| Introduced in version |
| 0.14 |
| See also |
| None |
Description
The Arch Stairs tool allows you to build several types of stairs automatically. Straight stairs (with or without a central landing) can be created from scratch. More complex stairs require base objects.
See the Stairs entry in wikipedia for a definition of the different terms used to describe parts of stairs.
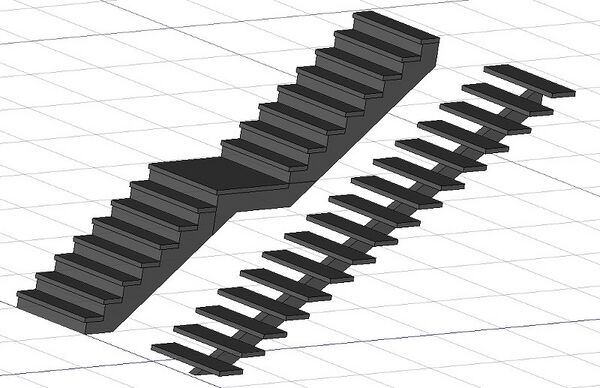
Two constructed stairs, one with a massive structure and a landing, the other with a single stringer.
Options
- Stairs share the common properties and behaviors of all Arch Components
Usage
- Optionally select one or more base objects, for example Draft Lines and Draft Wires:
- Draft Wires with two or more segments will be used to create landings. They must be on a plane parallel to the global XY plane. For example, select a U-shaped wire for a half-turn landing and an L-shaped wire for a corner landing.
- Draft Lines will be used to create flights.
- If the vertices of all lines and wires have correct Z coordinates, the created stairs will use this information.
- The base objects must be selected in the correct order starting with the bottom object.
- Press the
Stairs button, or press S, R keys.
- Adjust the desired properties. Some parts of the stairs, such as the structure, might not appear immediately, if any of the properties makes it impossible, such as a structure thickness of 0.
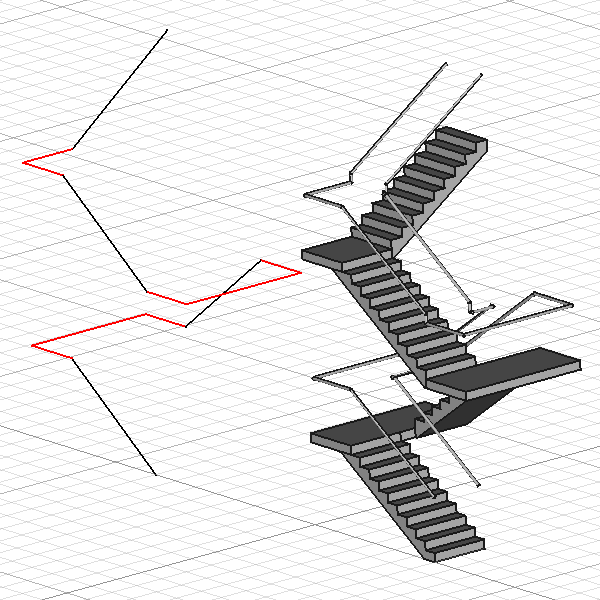
Complex stairs based on a selection of lines and wired as shown on the left.
In red the wires used for the landings at Z=1500mm, Z=3000mm and Z=4500mm.
In black the lines connecting them used for the flights.
Properties
Data
Segment and Parts
- DataAbs Top (
Vector): (read-only) The absolute top level the stairs lead to. - DataLast Segment (
Link): Last segment (flight or landing) of an Arch Stairs connecting to this segment. The start level of the stairs will be the end level of this last segment. - DataOutline Left (
VectorList): The left outline of the stairs. - DataOutline Left All (
VectorList): The left outline of all segments of the stairs. - DataOutline Right (
VectorList): The right outline of the stairs. - DataOutline Right All (
VectorList): The right outline of all segments of the stairs. - DataRailing Height Left (
Length): Height of the left railing of the stairs or landing. - DataRailing Height Right (
Length): Height of the right railing of the stairs or landing. - DataRailing Left (
LinkHidden): The left railing object. introduced in version 0.20: Property type updated fromStringtoLinkHidden. - DataRailing Offset Left (
Length): Offset of the left railing from the edge of the stairs or landing. - DataRailing Offset Right (
Length): Offset of the right railing from the edge of the stairs or landing. - DataRailing Right (
LinkHidden): The right railing object. introduced in version 0.20: Property type updated fromStringtoLinkHidden.
Stairs
- DataAlign (
Enumeration): The alignment of the stairs on the baseline. Only used if a baseline is defined. Can beLeft,RightorCenter. - DataHeight (
Length): The total height of the stairs. Only used if no baseline is defined, or if the baseline is horizontal. Ignored if DataRiser Height Enforce is non-zero. - DataLength (
Length): The total length of the stairs if no baseline is defined. Ignored if DataTread Depth Enforce is non-zero. - DataWidth (
Length): The width of the stairs. - DataWidth of Landing (
FloatList): If the DataNumber Of Steps is 1, the stairs object acts as a landing. When this is the case and the baseline is multi-segment, the width of first segment of the landing follows the DataWidth, the widths of subsequent segments follow the list set here.
Steps
- DataBlondel Ratio (
Float): (read-only) The calculated Blondel ratio. This ratio indicates comfortable stairs and should be between 62 and 64cm or 24.5 and 25.5in. - DataLanding Depth (
Length): The depth of the landing of the flight, if enabled in DataLandings. Defaults to the DataWidth if 0. - DataNosing (
Length): The size of the nosing. - DataNumber Of Steps (
Integer): The numbers of steps (risers). Must be at least 2 for a single flight, and at least 4 for a stairs with a central landing. - DataRiser Height (
Length): (read-only) The height of the risers. If DataRiser Height Enforce is 0 it is calculated (DataHeight / DataNumber of Steps). Else it is the same as DataRiser Height Enforce. - DataRiser Height Enforce (
Length): The enforced height of the risers. - DataRiser Thickness (
Length): The thickness of the risers. - DataTread Depth (
Length): (read-only) The depth of the treads. If DataTread Depth Enforce is 0 it is calculated (DataLength / DataNumber of Steps). Else it is the same as DataTread Depth Enforce. - DataTread Depth Enforce (
Length): The enforced depth of the treads. - DataTread Thickness (
Length): The thickness of the treads.
Structure
- DataConnection Down Start Stairs (
Enumeration): The type of connection between the lower floor slab and the start of the stairs. Can beHorizontalCut,VerticalCutorHorizontalVerticalCut. - DataConnection End Stairs Up (
Enumeration): The type of connection between the end of the stairs and the upper floor slab. Can betoFlightThicknessortoSlabThickness. - DataDown Slab Thickness (
Length): The thickness of the lower floor slab. - DataFlight (
Enumeration): The direction of the flight after the landing. Can beStraight,HalfTurnLeftorHalfTurnRight. - DataLandings (
Enumeration): The type of landings. Can beNoneorAt center(At each cornernot implemented yet). - DataStringer Overlap (
Length): The overlap of the stringers above the bottom of the treads. - DataStringer Width (
Length): The width of the stringers. - DataStructure (
Enumeration): The structure type of the stairs. Can beNone,Massive,One stringerorTwo stringers. - DataStructure Offset (
Length): The offset between the border of the stairs and the structure. - DataStructure Thickness (
Length): The thickness of the structure. - DataUp Slab Thickness (
Length): The thickness of the upper floor slab. - DataWinders (
Enumeration): The type of winders. Not implemented.
Limitations
- Only straight stairs are available at the moment
- See the forum entry for circle stairs.
- See the forum announcement.
Scripting
See also: Arch API and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
The Stairs tool can be used in macros and from the Python console by using the following function:
Stairs = makeStairs(baseobj=None, length=None, width=None, height=None, steps=None, name="Stairs")
- Creates a
Stairsobject from the givenbaseobj. - If
baseobjis not given, it will uselength,width,height, andsteps, to build a solid object.
Example:
import Arch
Stairs = Arch.makeStairs(length=5000, width=1200, height=3000, steps=14)
- 2D drafting: Sketch, Line, Polyline, Circle, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Fillet, Ellipse, Polygon, Rectangle, B-spline, Bézier curve, Cubic Bézier curve, Point
- 3D/BIM: Project, Site, Building, Level, Space, Wall, Curtain Wall, Column, Beam, Slab, Door, Window, Pipe, Pipe Connector, Stairs, Roof, Panel, Frame, Fence, Truss, Equipment
- Reinforcement tools: Custom Rebar, Straight Rebar, U-Shape Rebar, L-Shape Rebar, Stirrup, Bent-Shape Rebar, Helical Rebar, Column Reinforcement, Beam Reinforcement, Slab Reinforcement, Footing Reinforcement
- Generic 3D tools: Profile, Box, Shape builder..., Facebinder, Objects library, Component, External reference
- Annotation: Text, Shape from text, Aligned dimension, Horizontal dimension, Vertical dimension, Leader, Label, Axis, Axes System, Grid, Section Plane, Hatch, Page, View, Shape-based view
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid, Working Plane Top, Working Plane Front, Working Plane Side
- Modify: Move, Copy, Rotate, Clone, Create simple copy, Make compound, Offset, 2D Offset..., Trimex, Join, Split, Scale, Stretch, Draft to sketch, Upgrade, Downgrade, Add component, Remove component, Array, Path array, Polar array, Point array, Cut with plane, Mirror, Extrude..., Difference, Union, Intersection
- Manage: BIM Setup..., Views manager, Manage project..., Manage doors and windows..., Manage IFC elements..., Manage IFC quantities..., Manage IFC properties..., Manage classification..., Manage layers..., Material, Schedule, Preflight checks..., Annotation styles...
- Utils: Toggle bottom panels, Move to Trash, Working Plane View, Select group, Set slope, Create working plane proxy, Add to construction group, Split Mesh, Mesh to Shape, Select non-manifold meshes, Remove Shape from Arch, Close Holes, Merge Walls, Check, Toggle IFC Brep flag, Toggle subcomponents, Survey, IFC Diff, IFC explorer, Create IFC spreadsheet..., Image plane, Unclone, Rewire, Glue, Reextrude
- Panel tools: Panel, Panel Cut, Panel Sheet, Nest
- Structure tools: Structure, Structural System, Multiple Structures
- IFC tools: IFC Diff..., IFC Expand, Make IFC project, IfcOpenShell update
- Nudge: Nudge Switch, Nudge Up, Nudge Down, Nudge Left, Nudge Right, Nudge Rotate Left, Nudge Rotate Right, Nudge Extend, Nudge Shrink
- Additional: Preferences, Fine tuning, Import Export Preferences, IFC, DAE, OBJ, JSON, 3DS, SHP
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub