Arch Site
This page has been updated for that version.
|
|
| Menu location |
|---|
| 3D/BIM → Site |
| Workbenches |
| BIM |
| Default shortcut |
| S I |
| Introduced in version |
| - |
| See also |
| None |
Description
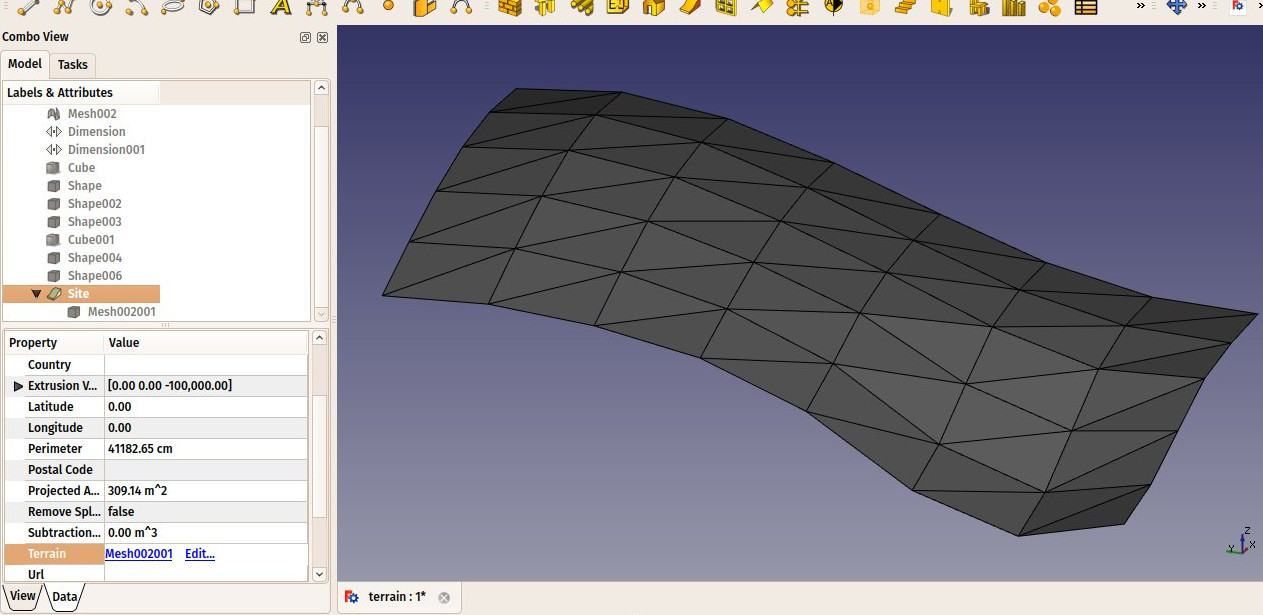
The Arch Site is a special object that combines properties of a standard FreeCAD group object and Arch objects. It is particularly suited for representing a whole project site, or terrain. In IFC-based architectural work, it is mostly used to organize your model, by containing building objects. The site is also used to manage and display a physical terrain, and can compute volumes of earth to be added or removed.
Usage
- Optionally, select one or more objects to be included in your new site.
- Press the
Site button, or press the S then I keys.
Options
- After creating a site, you can add objects to it by drag and dropping them in the Tree view or by using the
Arch Add tool. This only determines which objects are part of the given site, and has no effect on the terrain.
- You can remove objects from a site by drag and dropping them out of it in the Tree view or by using the
Arch Remove tool.
- You can add a terrain object by editing the Site's DataTerrain property. The terrain can be an open shell or (introduced in version 0.21) a solid.
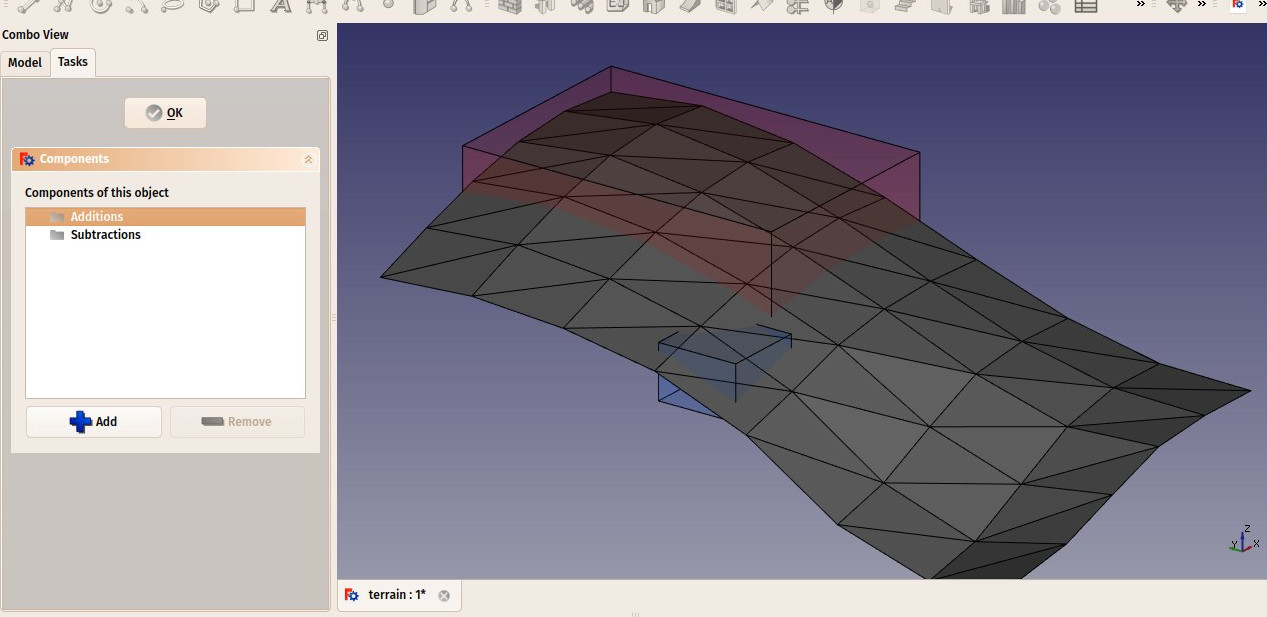
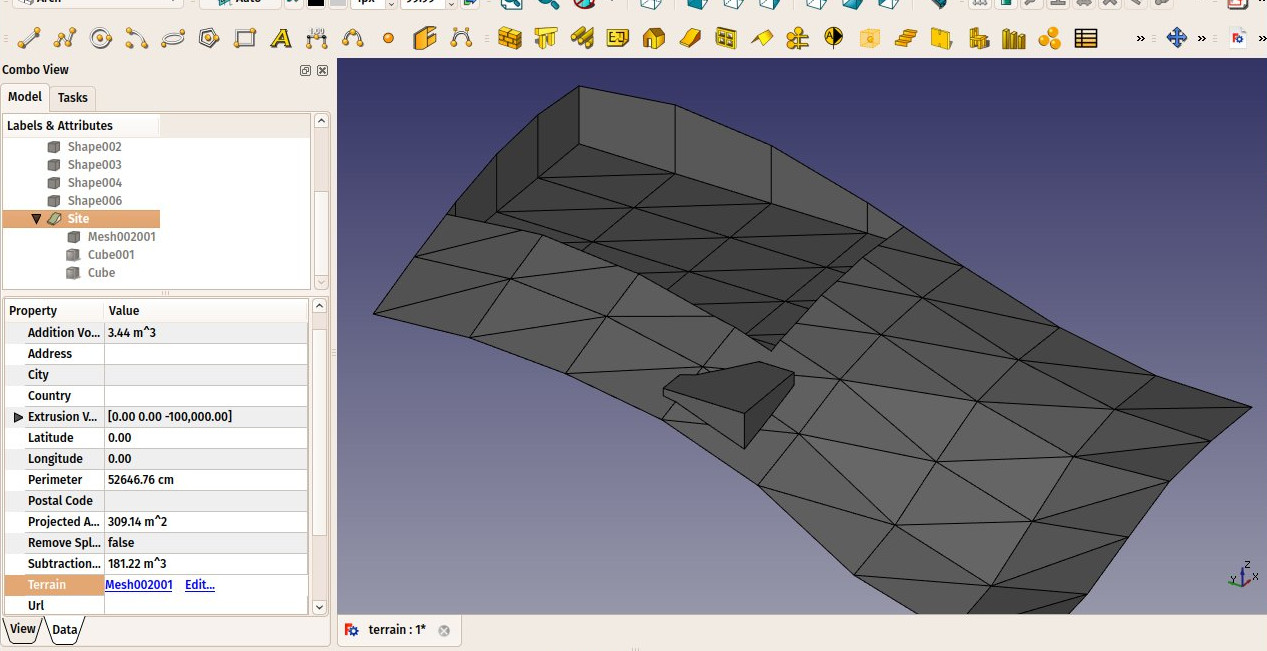
- You can add volumes to be added or subtracted from the base terrain, by double-clicking the Site, and adding objects to its Additions or Subtractions groups. The objects must be solids.
- The DataExtrusion Vector property can be used to solve some problems that can appear when the terrain is an open shell and there are additions and/or subtractions. In order to perform those additions/subtractions, the open shell is extruded into a solid, which is then appropriately unioned/subtracted. Depending on the terrain topology, this extrusion might fail with the default extrusion vector. You might then be able to remedy the problem by changing this to a different value. This property is ignored if the terrain is a solid.
Properties
Data
- DataTerrain: The base terrain of this site
- DataAddress: The street and housenumber of this site
- DataPostal Code: The postal or zip code of this site
- DataCity: The city of this site
- DataCountry: The country of this site
- DataLatitude: The latitude of this site
- DataLongitude: The longitude of this site
- DataUrl: An url that shows this site in a mapping website
- DataProjected Area: The area of the projection of this object onto the XY plane
- DataPerimeter: The perimeter length of this terrain
- DataAddition Volume: The volume of earth to be added to this terrain
- DataSubtraction Volume: The volume of earth to be removed from this terrain
- DataExtrusion Vector: An extrusion vector to use when performing boolean operations
- DataRemove Splitter: Remove splitters from the resulting shape
- DataDeclination: The angle between the true North and the North direction in this document, that is, the Y axis. This means that by default North points to the Y axis, and East to the X axis; the angle increments counterclockwise. This property was previously known as DataNorth Deviation.
- DataEPW File: Allow to attach an EPW file from the Ladybug EPW data website to this site. This is needed to display wind rose diagrams
View
- ViewSolar Diagram: Shows or hides the solar diagram
- ViewSolar Diagram Color: The color of the solar diagram
- ViewSolar Diagram Position: The position of the solar diagram
- ViewSolar Diagram Scale: The scale of the solar diagram
- ViewWind Rose: Shows or hides the wind rose diagram (requires the EPW File data property filled, and the Ladybug Python module installed (see below)
Typical workflow
Start by creating an object that represents your terrain. For example, it is easy to import mesh data, that can be turned into a Part Shape from menu Part → Create Shape from Mesh. Then, create a Site object, and set its DataTerrain property to the Part we just created:
Create some volumes (they must be solids) that represent the areas that you wish to be excavated or filled. Double-click the Site object in the Tree View, and add these volumes to the Additions or Subtractions groups. Click OK.
The site geometry will be recomputed and the areas, perimeter, and volumes properties recalculated.
Solar and wind diagrams
If Ladybug is installed on your system, Arch Sites can display a solar diagram and/or a wind rose. For this, DataLongitude, DataLatitude and DataDeclination (previously DataNorth Deviation) must be correctly set, and ViewSolar Diagram or ViewWind Rose set to true.
Note: If you don't have Ladybug, pysolar is still supported to generate solar diagrams, but not wind roses. Pysolar 0.7 or above is required; this version only works with Python 3. If you require this feature with Python 2, you should have Pysolar 0.6 as this is the last version that works with Python 2. However, Ladybug is a much more powerful tool that will probably be used more in the future, so we recommend using it instead of pysolar. Ladybug can be installed simply via pip.
Scripting
See also: Arch API and FreeCAD Scripting Basics.
The Site tool can be used in macros and from the Python console by using the following function:
Site = makeSite(objectslist=None, baseobj=None, name="Site")
- Creates a
Siteobject fromobjectslist, which is a list of objects, orbaseobj, which is aShapeorTerrain.
Example:
import FreeCAD, Draft, Arch
p1 = FreeCAD.Vector(0, 0, 0)
p2 = FreeCAD.Vector(2000, 0, 0)
baseline = Draft.makeLine(p1, p2)
Wall = Arch.makeWall(baseline, length=None, width=150, height=2000)
FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.recompute()
Building = Arch.makeBuilding([Wall])
Site = Arch.makeSite([Building])
FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.recompute()
FreeCAD.Gui.ActiveDocument.ActiveView.viewIsometric()
Solar diagram
As long as the pysolar module is present, a solar diagram can be added to the site. Set the longitude, latitude and declination angles as appropriate, as well as an adequate scale for the size of your model.
Please note that Pysolar 0.7 or above is required, and this version only works with Python 3.
Site.Longitude = -46.38
Site.Latitude = -23.33
Site.Declination = 30
#Site.Compass = True
Site.ViewObject.SolarDiagram = True
Site.ViewObject.SolarDiagramScale = 10000
FreeCAD.ActiveDocument.recompute()
Solar diagram independent of Site
A solar diagram can be created with the following function, independently of any site.
Node = makeSolarDiagram(longitude, latitude, scale=1, complete=False)
- Creates a solar diagram as a Pivy node, using
longitudeandlatitude, with an optionalscale. - If
completeisTrue, the 12 months are drawn, which shows the full solar analemma.
import FreeCADGui, Arch
Node = Arch.makeSolarDiagram(-46.38, -23.33, scale=10000, complete=True)
FreeCAD.Gui.ActiveDocument.ActiveView.getSceneGraph().addChild(Node)
- 2D drafting: Sketch, Line, Polyline, Circle, Arc, Arc by 3 points, Fillet, Ellipse, Polygon, Rectangle, B-spline, Bézier curve, Cubic Bézier curve, Point
- 3D/BIM: Project, Site, Building, Level, Space, Wall, Curtain Wall, Column, Beam, Slab, Door, Window, Pipe, Pipe Connector, Stairs, Roof, Panel, Frame, Fence, Truss, Equipment
- Reinforcement tools: Custom Rebar, Straight Rebar, U-Shape Rebar, L-Shape Rebar, Stirrup, Bent-Shape Rebar, Helical Rebar, Column Reinforcement, Beam Reinforcement, Slab Reinforcement, Footing Reinforcement
- Generic 3D tools: Profile, Box, Shape builder..., Facebinder, Objects library, Component, External reference
- Annotation: Text, Shape from text, Aligned dimension, Horizontal dimension, Vertical dimension, Leader, Label, Axis, Axes System, Grid, Section Plane, Hatch, Page, View, Shape-based view
- Snapping: Snap lock, Snap endpoint, Snap midpoint, Snap center, Snap angle, Snap intersection, Snap perpendicular, Snap extension, Snap parallel, Snap special, Snap near, Snap ortho, Snap grid, Snap working plane, Snap dimensions, Toggle grid, Working Plane Top, Working Plane Front, Working Plane Side
- Modify: Move, Copy, Rotate, Clone, Create simple copy, Make compound, Offset, 2D Offset..., Trimex, Join, Split, Scale, Stretch, Draft to sketch, Upgrade, Downgrade, Add component, Remove component, Array, Path array, Polar array, Point array, Cut with plane, Mirror, Extrude..., Difference, Union, Intersection
- Manage: BIM Setup..., Views manager, Manage project..., Manage doors and windows..., Manage IFC elements..., Manage IFC quantities..., Manage IFC properties..., Manage classification..., Manage layers..., Material, Schedule, Preflight checks..., Annotation styles...
- Utils: Toggle bottom panels, Move to Trash, Working Plane View, Select group, Set slope, Create working plane proxy, Add to construction group, Split Mesh, Mesh to Shape, Select non-manifold meshes, Remove Shape from Arch, Close Holes, Merge Walls, Check, Toggle IFC Brep flag, Toggle subcomponents, Survey, IFC Diff, IFC explorer, Create IFC spreadsheet..., Image plane, Unclone, Rewire, Glue, Reextrude
- Panel tools: Panel, Panel Cut, Panel Sheet, Nest
- Structure tools: Structure, Structural System, Multiple Structures
- IFC tools: IFC Diff..., IFC Expand, Make IFC project, IfcOpenShell update
- Nudge: Nudge Switch, Nudge Up, Nudge Down, Nudge Left, Nudge Right, Nudge Rotate Left, Nudge Rotate Right, Nudge Extend, Nudge Shrink
- Additional: Preferences, Fine tuning, Import Export Preferences, IFC, DAE, OBJ, JSON, 3DS, SHP
- Getting started
- Installation: Download, Windows, Linux, Mac, Additional components, Docker, AppImage, Ubuntu Snap
- Basics: About FreeCAD, Interface, Mouse navigation, Selection methods, Object name, Preferences, Workbenches, Document structure, Properties, Help FreeCAD, Donate
- Help: Tutorials, Video tutorials
- Workbenches: Std Base, Assembly, BIM, CAM, Draft, FEM, Inspection, Material, Mesh, OpenSCAD, Part, PartDesign, Points, Reverse Engineering, Robot, Sketcher, Spreadsheet, Surface, TechDraw, Test Framework
- Hubs: User hub, Power users hub, Developer hub